Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
The Non-cooperation Movement began on which one of the following dates?
(a) January 1921
(b) November 1921
(c) December 1921
(d) May 1921
Answer
Answer: (a) January 1921
Question 2.
In which of the following places Mahatma Gandhi organised satyagraha for the
first time in India?
(a) Dandi
(b) Ahmedabad
(c) Kheda
(d) Champaran
Answer
Answer: (d) Champaran
Question 3.
Who among the following was associated with the formation of Swaraj Party
within the Congress?
(a) Subhas Chandra Bose
(b) Motilal Nehru
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru
(d) Dadabhai Naoroji
Answer
Answer: (b) Motilal Nehru
Question 4.
In which of the following Indian National Congress sessions was the demand
of‘Purna Swaraj’ formalised in December 1929?
(a) Madras Session
(b) Lahore Session
(c) Calcutta Session
(d) Nagpur Session
Answer
Answer: (b) Lahore Session
Question 5.
Who organised the dalits into the Depressed classes Association?
(a) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Motilal Nehru
Answer
Answer: (a) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Question 6.
Why had the Congress ignored the dalits for long?
(a) Due to their liberal outlook
(b) Due to fear from the Britishers
(c) For fear of offending the sanatanis
(d) For fear of Dr B.R. Ambedkar
Answer
Answer: (c) For fear of offending the sanatanis
Question 7.
Who created the first image of Bharat Mata?
(a) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
(b) Subhash Chandra Bose
(c) Rabindranath Tagore
(d) Abanindranath Tagore
Answer
Answer: (a) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
Question 8.
Which of the following combination of colours was there in the ‘Swaraj flag’
designed by Gandhiji in 1921?
(a) red, green and white
(b) red, green and yellow
(c) orange, white and green
(d) yellow, white and green
Answer
Answer: (a) red, green and white
Question 9.
Who announced a vague offer of‘Dominion Status’ for India in 1929?
(a) Lord Curzon
(b) Viceroy Irwin
(c) Lord William Bentick
(d) Lord Mountbalten
Answer
Answer: (b) Viceroy Irwin
Question 10.
Which of the following agreements gave reserved seats to the ‘Depressed
classes’ in provincial and central legislative councils?
(a) Lucknow Pact
(b) Gandhi Irwin Pack
(c) Poona Pact
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Poona Pact
Question 11.
In which year the Second Round Table Conference was held?
(a) 1931
(b) 1935
(c) 1938
(d) 1945
Answer
Answer: (a) 1931
Explanation:
In December 1931, Gandhiji attended the second round table conference by
demanding separate electorates for dalit.
Question 12.
What was the demand of 1929 sessions of the Congress at Lahore ?
(a) Poorna Swaraj
(b) Right to speech
(c) Half authority
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Poorna Swaraj
Question 13.
Who started the Swaraj Party?
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) C.R.Das
(d) C.R. Das and Motilal Nehru.
Answer
Answer: (d) C.R. Das and Motilal Nehru.
Explanation:
C. R. Das and Motilal Nehru formed the Swaraj Party because they wanted to
enter the Provincial Councils and oppose British policies.
Question 14.
Why was the slogans demanding “Swatantra Bharat” important?
(a) It showed the greatness of Mahatma Gandhi
(b) They were going beyond their own locality and emotionally identifying with
an all-India movement
(c) They were a unifying force of the Non-Cooperation Movement
(d) The various ways in which ‘Swaraj’ was interpreted by different people
Answer
Answer: (b) They were going beyond their own locality and emotionally
identifying with an all-India movement
Explanation:
When the tribals chanted Gandhiji’s name and raised slogans demanding
‘Swatantra Bharat’, they were also emotionally relating to an all-India
agitation. They were going beyond their own locality and emotionally
identifying with an all-India movement.
Question 15.
When did the Jallianwalla Bagh incident take place?
(a) On 13 April
(b) On 15 August
(c) On 27 October
(d) On 10 March
Answer
Answer: (a) On 13 April
Explanation:
On 13 April the Jallianwalla Bagh incident took place. On that day a large
crowd gathered in the enclosed ground of Jallianwalla Bagh, unaware of the
martial law that had been imposed. Dyer entered the area, blocked the exit
points, and opened fire on the crowd, killing hundreds.
Question 16.
What were boycotted during Non-cooperation movement?
(a) Foreign goods
(b) Food
(c) Water
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Foreign goods
Explanation:
At the time of Non-cooperation movement foreign goods were boycotted as the
symbol of foreign trade and it begins with the surrender of titles that the
government awarded, and a boycott of civil services, army, police, courts
and legislative councils and schools.
Question 17.
Who published ‘The Folklore of Southern India’?
(a) Natesa Sastri
(b) Dr.Ambedkar
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Natesa Sastri
Explanation:
In Madras, Natesa Sastri published a massive four-volume collection of Tamil
folk tales, The Folklore of Southern India.
Question 18.
What was the reason for Mahatma Gandhiji’s fast unto death in 1932?
(a) The clash with Dr. Ambedkar
(b) The Clash with Bose
(c) The clash with Nehru
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) The clash with Dr. Ambedkar
Explanation:
The clash with Dr Ambedkar over his demand for a separate electorate for
Dalits which he thought would halt their integration into society, led
mahatma Gandhi to do fast unto death in 1932.
Question 19.
Who was the two great writers of Bengal and Madras, who contributed to
nationalism in the late nineteenth century?
(a) Rabindranath Tagore and Natesa Sastri
(b) Jamini Roy and Ravi Verma
(c) Rabindranath Tagore and Ravi Verma
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Rabindranath Tagore and Natesa Sastri
Explanation:
The two great writers of Bengal and Madras, who contributed to nationalism
in the late nineteenth century through folklore, were Rabindra Nath tagore
and Natesa Sastri
Question 20.
Who was the President of the Muslim League in 1930?
(a) Mr. M.A. Jinnah
(b) Maulana Azad
(c) Abdul Ghaffar Khan
(d) Sir Muhammad Iqbal
Answer
Answer: (d) Sir Muhammad Iqbal
Explanation:
In 1930, Sir Muhammad Iqbal, as president of the Muslim League, reiterated
the importance of separate electorates for the Muslims as an important
safeguard for their minority political interests.
Question 21.
The Non-Cooperation Movement was started by Mahatma Gandhi in support of which
movement?
(a) Khilafat
(b) Swaraj
(c) Khilafat and Swaraj
(d) none of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Khilafat and Swaraj
Explanation:
At the Calcutta session of the Congress in September 1920, he convinced
other leaders of the need to start a non-cooperation movement in support of
Khilafat as well as for Swaraj.
Question 22.
Who was the author of the famous novel ‘Anandamath’?
(a) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
(b) Abanindranath Tagore
(c) Natesa Sastri
(d) Rabindranath Tagore
Answer
Answer: (a) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
Explanation:
Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay was the author of the famous novel
‘Anandamath’. In the 1870s he wrote ‘Vande Mataram’ as a hymn to the
motherland. His novel Anandamath and widely sung during the Swadeshi
movement in Bengal.
Question 23.
What was the reason behind clash between Gandhi Ji and Dr Ambedkar?
(a) Separate electorates would create division in the society.
(b) Separate electorates would slow down the progress of integration into
society.
(c) With separate electorates, Dalit’s would gain respect in society.
(d) The condition of Dalit’s would become better.
Answer
Answer: (a) Separate electorates would create division in the society.
Explanation:
Gandhiji began fast unto death when Dr. B.R. Ambedkar demanded separate
electorate for dalits because Separate electorates would create division in
the society.
Question 24.
When did Gandhiji travelled to Champaran in Bihar?
(a) 1916
(b) 1920
(c) 1925
(d)1918
Answer
Answer: (a) 1916
Explanation:
In 1916 he travelled to Champaran in Bihar to inspire the peasants to
struggle against the oppressive plantation system.
Question 25.
Which one of the following leaders headed Oudh Kisan Sabha?
(a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Subhash Chandra Bose
(d) Motilal Nehru
Answer
Answer: (a) Jawahar Lal Nehru
Explanation:
By October, the Oudh Kisan Sabha was set up headed by Jawaharlal Nehru, Baba
Ramchandra and a few others. Within a month, over 300 branches had been set
up in the villages around the region.
Picture-based Questions:
Question 1.
Identify the following personality (NCERT TB page 70) and write a short
paragraph on him highlighting his contribution to the Indian national
movement.

Answer
Answer:
This is the portrait of Bal Gangadhar Tilak, a great leader of Indian
national movement. He played a very significant role in national movement.
Indian National Congress was divided into two wings- Moderate and Extremist.
He was the first extremist leader who declared “Swaraj is my birth right and
I must have it”. He organised the nationalist movement in Maharashtra and
brought it in conflict with the British government.
He united the moderates and extremists of Congress Party. He appealed Indian people to boycott British goods, British courts, schools and colleges. He was sent to jail numerous times by the Britishers. He infused the spirit of self sacrifice among the Indian masses. Movement. Thus his contribution paved a new path to the Indian national movement.
Question 2.
Look at the picture taken from NCERT Textbook Page 71 and answer the questions
that follow.
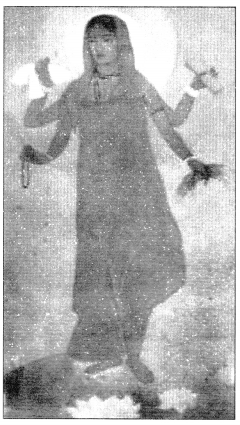
(i) What is this image of?
(ii) Who painted this image and when?
(iii) How does the painter portray Bharat Mata?
Answer
Answer:
(i) This is the image of Bharat Mata.
(ii) Abanindranath Tagore painted this image in 1905.
(iii) The painter portrays Bharat Mata as an ascetic figure. She is calm,
composed, divine and spiritual.
Question 3.
Look at the picture taken from NCERT Textbook Page 72 and answer the questions
that follow.

(i) What is depicted in the above picture?
(ii) What was its significance during the freedom struggle?
Answer
Answer:
(i) In this picture, Bharat Mata is shown with a trishul standing beside a
lion and an elephant. These are the symbols of power and authority.
(ii) The image of Bharat Mata was an icon to create nationalist feeling in
Indians during the freedom struggle. It shows that Indians should fight
against the Britishers vehemently.
How do you think to help the depressed classes in India? Express your opinion.
Answer
Answer:
The depressed classes should be helped in India by the government NGOs and
the society. At first, they must be given moral support so that they may
come into the mainstream of the society. They must be provided educational
facilities. This way they may come into the public and private sectors and
their representation may be felt in the society. In politics they must be
given proper representation.
Social Science Quiz Nationalism in India Class 10
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following agreements gave seats to the depressed classes in Provincial and Central Legislative council? [AI 2012]
(a) Lucknow Pact
(b) Gandhi-irwin Pact
(c) Poona Pact
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Poona Pact
2. Which one of the following Viceroys announced a vague offer of dominion status for India in October 1929? [AI 2012]
(a) Lord Mount batter
(b) Lord Dalhousie
(c) Lord Irwin
(d) None of these
3. Which one of the following combination of colours was there in the Swaraj flag designed by Gandhiji in 1921? [AI 2012]
(a) Red, Green and White
(b) Red, Green and Yellow
(c) Orange, White and Green
(d) Yellow, White and Green
4. In which of the following region was Dalit participa¬tion limited in the civil disobedience movement? [AI 2012]
(a) Maharashtra and Nagpur
(b) Awadh and Maharashtra
(c) Bengal and Punjab
(d) Kerala and Karnataka
5. Why were the Dalits ignored by the Congress for a longtime? [AI 2012]
(a) Fear of offending the sanatanis
(b) Fear from Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) Fear from socialism
(d) Fear from industralists
6. Which of the following Acts did not permit plantation workers to leave the tea gardens without permission? [AI 2012]
(a) Indian Independence Act
(b) Inland Emigration Act of 1859
(c) Impaired Legislature Council Act
(d) Inland Immigration Act
7. In which of the following year Mahatma Gandhi inspired the peasants of Champaran district of Bihar to struggle against the oppressive plantation system ?
(a) 1916
(b) 1917
(c) 1918
(d) 1919
8. In which one of the following Indian National Congress Session, the idea of Non-Cooperation movement was accepted ?
(a) Lahore Session
(b) Nagpur Session
(c) Calcutta (Kolkata) Session
(d) Madras (Chennai) Session
9. Why did Gandhiji withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement ? [Delhi 2011]
(a) Gandhiji realised that people were losing interest in the movement.
(b) Gandhiji felt the movement was turning violent in many places.
(c) Some Congress leaders wanted to participate in elections to Provincial Councils.
(d) Some Congress leaders wanted more radical mass agitations.
10. Which one of the following statements is false about Alluri Sitaram Raju? [Delhi 2011]
(a) He claimed he had special powers.
(b) He was inspired by the non-cooperation movement.
(c) He believed in the principle of non-violence advocated by Gandhiji.
(d) He persuaded people to give up drinking.
11. Which one of the following statements is not related to the Gandhi-irwin Pact? [AI 2011]
(a) Gandhiji agreed not to launch any further mass agitations against the British.
(b) Gandhiji agreed to participate in the Round Table Conference.
(c) Gandhiji decided to call off the Civil Disobedience Movement.
(d) The British agreed to release the political prisoners.
12. Why did Nationalists in India tour villages to gather folk songs and legends ? Choose the most appropriate reason from the following : [AI 2011]
(a) Nationalists wanted to study their own culture.
(b) Nationalists wanted to publish it and earn money.
(c) Nationalists did it because it gave a true picture of traditional culture.
(d) Nationalists wanted to keep folk culture intact.
13. Who among the following wrote ‘Vande Mataram’? [Foreign 2011]
(a) Abanindranath Tagore
(b) Rabindranath Tagore
(c) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
(d) Natesa Shastri
14. Which of the following statements is not true about the Simon Commission? [Foreign 2011]
(a) It was appointed by Sir John Simon.
(b) It did not have any Indian member.
(c) It was opposed by all parties in India.
(d) It was set up to look into the Constitutional system in India.
15. The Jallianwalla Bagh incident took place in the city of
(a) Amritsar
(b) Agra
(c) Meerut
(d) Lahore
16. Which of the following was the reason for calling off the Non-Cooperation Movement by Gandhiji ?
(a) His arrest
(b) The Chauri-Chaura incident
(c) Pressure from the British Government
(d) Round Table Conference
17. The resolution of Puma Swaraj was adopted at which session?
(a) Karachi Congress
(b) Haripur Congress
(c) Lahore Congress
(d) Lucknow Congress
18. The Simon Commission was boycotted because
(a) there was no Indian in the commission
(b) it supported the Muslim League
(c) Congress felt that the people deserved Swaraj
(d) there were differences among the members.
19. When did Jallianwalla Bagh incident take place ?
(a) 13th April 1919
(b) 14th April 1920
(c) 13th March 1919
(d) 15th March 1920
20. Justice Party of Madras was a party of
(a) non-muslims
(b) non-brahmins
(c) non-tamils
(d) judges
21. Who led a peasant movement during the Non-Cooperation Movement ?
(a) Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) Gandhiji
(c) Baba Ramchandra
(d) Sardar Patel
22. Baba Ramchandra led a Peasant Movement in Avadh against the
(a) British government
(b) the ruler of Avadh
(c) the Talukdars
(d) the moneylenders
23. By whom was the Swaraj Party formed?
(a) Motilal Nehru and C.R. Das
(b) Subhas Chandra Bose and Sardar Patel
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru and Rajendra Prasad
(d) Motilal Nehru and Rajendra Prasad
24. With which main demand did the Civil Disobedience Movement start ?
(a) Abolition of Untouchability
(b) Abolition of Dowry
(c) Abolition of Salt Law
(d) None of the above
25. At which of the following places did Gandhiji make salt out of sea water to defy the salt law ?
(a) Sabarmati
(b) Wardha
(c) Dandi
(d) Ahmedabad
26. Who among the following led the Civil Disobedience Movement in Peshawar ?
(a) Lala Lajpat Rai
(b) Maulana Abul Kalam Azad
(c) Khan Abdul Gaffar Khan
(d) Jawaharlal Nehru
27. By what name were the dalits referred by Gandhiji ?
(a) Untouchables
(b) Shudras
(c) Harijans
(d) Achhuts
28. When was the Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industries set up ?
(a) 1926
(b) 1927
(c) 1928
(d) 1929
29. Why was Alluri Sitaram Raju well known ?
(a) He led the militant movement of tribal peasants in Andhra Pradesh
(b) He led a peasant movement in Avadh
(c) He led a satyagraha movement in Bardoli
(d) He set up an organisation for the uplifment of the dalits.
30. Who organised the dalits into the Depressed Classes Association in 1930 ?
(a) Sitaram Raju
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) Mahatma Gandhi
(d) Sardar Patel
31. By whom was the song ‘Vande Mataram’ written ?
(a) Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay
(b) Rabindranath Tagore
(c) Sarat Chandra
(d) Natesa Sastri
32. Which of the following was the most important feature of Satyagraha Movement advocated by Gandhiji ?
(a) Abolition of untouchability
(b) Social equality
(c) Truth and non-violence
(d) Basic education
33. Why did Gandhiji organise Satyagraha in 1917 in Kheda district of Gujarat ?
(a) To support the plantation workers.
(b) To protest against high revenue demand.
(c) To support the mill workers to fulfil their demand.
(d) To demand loans for the farmers.
34. Gandhiji organised Satyagraha against Rowlatt Act in 1919 because
(a) the Act was unjust, which denied the civil rights to Indians.
(b) the Act was passed by the British.
(c) the Act discriminated against the Muslims.
(d) the Act denied educational rights to Indians.
35. Why was Satyagraha organised in Champaran in 1916 ?
(a) To oppose the British laws.
(b) To oppose the plantation system.
(c) To oppose high land revenue.
(d) To protest against the oppression of the mill workers.
36. Why did the Indians oppose the Rowlatt Act ?
(a) It introduced the Salt Law.
(b) It increased taxes on land.
(c) It gave the British the power to arrest and detain a person without a trial.
(d) It put a ban on the Congress party.
37. Why did Gandhiji organise a Satyagraha in Ahmedabad Mill in 1918 ?
(a) To protest against the poor working conditions in the factory.
(b) To demand for higher wages for workers.
(c) To protest against high revenue demand.
(d) None of the above.
38. Who among the following two leaders led the Khilafat Movement ?
(a) Shaukat Ali and Muhammad AM
(b) Gandhiji and Sardar Patel
(c) Muhammad Ali Jinnah and Abul Kalam Azad
(d) Abul Kalam Azad and Jawaharlal Nehru
39. What is meant by begar ?
(a) Unemployment
(b) Forced labour without payment
(c) Beggary
(d) Working for nominal payment
40. ‘Hind Swaraj’ was written by
(a) Abul Kalam Azad
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Sardar Patel
(d) Subhas Chandra Bose
41. What does the term Khalifa refer ?
(a) Sultan of a Muslim country
(b) Spiritual leader of the Muslims
(c) Nawab of a Muslim state
(d) Badshah of Mughal period
42. Mark the correct response
Under the Inland Emigration Act of 1859 the peasants were not permitted to
(a) leave their village
(b) settle in the city
(c) leave their plantation without permission
(d) allow the women to leave farmlands without permission
43. Why did Mahatma Gandhi decide to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement ?
(a) The leaders failed to organise the movement well
(b) People lacked courage
(c) The movement turned violent
(d) The movement was not widespread enough to continue
44. Why was the Simon Commission sent to India ?
(a) To look into the Indian constitutional matter and suggest reform
(b) To choose members of Indian Council
(c) To settle disputes between the government and the Congress leaders
(d) To set up a government organisation
45. Why was the Round Table Conference held in England ?
(a) To discuss the provisions of future Indian Constitution.
(b) To discuss the steps to be taken to check Indian National Movement.
(c) To give concessions to Indians
(d) To make plans for improvement of agriculture in India.
46. By whom was the first image of Bharatmata painted ?
(a) Rabindranath Tagore
(b) Abanindranath Tagore
(c) Ravi Verma .
(d) Nandalal Bose
47. During which of the following movements did the women participate in large numbers for the first time ?
(a) Swadeshi and Boycott Movement
(b) Non-Cooperation Movement
(c) Civil Disobedience Movement
(d) Quit India Movement
48. What kind of movement was launched by the tribal peasants of Gudem Hills in Andhra Pradesh ?
(a) Satyagraha Movement
(b) Militant Guerrilla Movement
(c) Non-Violent Movement
(d) None of the above.
49. Which of the following is the most important factor for the growth of nationalism in India ?
(a) British administrative reforms.
(b) Introduction of railways.
(c) Social reforms.
(d) Colonial exploitation under the British rule.
50. Why did General Dyer open fire on peaceful crowd in Jallianwalla Bagh?
Mark the most important factor
(a) To punish the Indians.
(b) To take revenge for breaking martial laws.
(c) To create a feeling of terror and awe in the mind of Indians.
(d) To disperse the crowd.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10
Social Science History Chapter 3 Nationalism in India
Q.1. Explain:
(a) Why is the growth of nationalism in the colonies linked to an anti-colonial movement ?
(b) How did the First World War help in the growth of the National Movement in India? [CBSE2014]
Or
Explain any four facts to show how did the First World War help in the growth of the National Movement in India. [CBSE March 2011]
(a) Why were Indians outraged by the Rowlatt Act ?
(b) Why did Gandhiji decide to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement?
Ans. (a) The growth of Modern nationalism in the colonies is linked to an anti-colonial movement due to the factors as mentioned below :
- People began discovering their unity in the process of their struggle with colonialism. The sense of being oppressed under colonialism provided a shared bond that tied many different groups together.
- As each class and group felt the effects of colonialism differently, their experiences were varied and their notions of freedom were not always the same, so the Congress under Mahatma Gandhi tried to forge these groups together within one movement.
- Thus, in spite of differences and conflicts, different groups and communities came under the banner of Indian National Congress and took part in various movements which were anti¬colonial or against the British.
(b) The First World War helped in the growth of the National Movement in India as it created a new economic and political situation as mentioned below :
- The defense expenditure had increased.
- War loans were taken and more taxes were imposed.
- Custom duties were raised.
- Income tax was introduced.
- The rise in prices led to extreme hardships for the people.
- There was widespread discontentment in the rural area due to forced recruitment of soldiers.
- In 1918-19 and 1920-21 crops failed in many parts of India resulting in acute shortages of food.
- There was influenza epidemic too. According to the Census of 1921, twelve to thirteen million people perished as a result of famines and epidemics. People thought that their hardships and suffering would come to an end after the war but that did not happen. So these factors were responsible for the rise of nationalism in India.
(c) Indians were outraged by the Rowlatt Act (1919) due to the following reasons :
- They had hoped that after the war their hardships would be over and the government would take steps to improve their condition.
- On the other hand, the government got the Rowlatt Act passed in the Imperial Legislative Council against the united opposition of the Indian members.
- The Act gave the government enormous powers to repress political activities. It allowed detention of political prisoners without trial for two years.
- These provisions meant the suspension of two principles of justice – trial by jury and habeas corpus – the rights safeguarding against illegal imprisonment.
- The Rowlatt Act was considered as Black Law and the Indians under the leadership of Gandhi decided to oppose it by non-violent civil disobedience which would start with a hartal on 6 April.
(d) Gandhiji decided to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement due to the reasons as mentioned below :
- The movement was turning violent in many places.
- Gandhiji thought that Satyagrahis needed to be properly trained before they would be ready for mass struggles. This was in context of the incident in Chauri-Chaura, a village in Gorakhpur district UP where twenty two policemen were brutally killed after they had fired on a political procession.
- There had been disturbances in Madras and Calcutta also. The above factors made it clear that the country was not yet ready of mass movement. So Gandhiji prevailed upon the Congress Working Committee to call off the movement.
Q.2. What is meant by the idea of Satyagraha?
Or
Explain the idea of Satyagraha according to Gandhiji. [CBSE 2014 (D)]
Ans.
- Satyagraha is pure soul-force.
- Truth is the very substance of the soul. That is why this force is called Satyagraha.
- The soul is informed with knowledge. It burns the flame of love.
- Non-violence is the supreme dharma.
- The idea of Satyagraha emphasised the power of truth and the need to search for truth. It suggested that if the cause was true, if the struggle was against injustice, then the physical force was not necessary to fight the oppressor.
- Without seeking vengeance or being aggressive, a satyagrahi could win the battle through non-violence.
- In Satyagraha, people including the oppressors – had to be persuaded to see the truth, instead of being forced to accept truth through the use of violence.
- In this way by this struggle, truth was bound to ultimately triumph. Mahatma Gandhi believed that this dharma of non-violence would unite all Indians.
Q.3. Write a newspaper report on :
(a) The Jallianwala Bagh massacre
(b) The Simon Commission
Ans. (a) The Jallianwala Bagh massacre: A public meeting was announced for the 13th April 1919, at Jallianwala Bagh, Amritsar to protest against the Rowlatt Act. The people were allowed to assemble there. After they had gathered there in thousands, General Dyer marched there with armoured cars and troops. Without giving any warning to the people to disperse, he ordered firing on the unarmed, and peaceful people. The casualties among the Indians were very heavy. Dyer’s purpose in doing so was to ‘produce a moral effect’, to create in the minds of Satyagrahis, a feeling of terror and awe. This massacre of innocent people in thousands converted Mahatma Gandhi into a non-cooperator.
(b) (i) The Indian members of the Central Legislative Assembly exposed the drawbacks in the Government of India Act of 1919 A.D. As a result of it, the Simon Commission was appointed in 1927 A.D. to suggest any further constitutional reforms. This commission consisted of seven members and its Chairman was Sir John Simon.
(ii) Why was it boycotted by the Indians?
But Indians boycotted the Simon Commission because there was no Indian member in this commission. The terms of the commission’s appointment did not give any indication of ‘Swaraj’, while the demand of the Indians was only ‘Swaraj’. Therefore, the Indian National Congress, the Muslim League, and other parties decided to oppose the Simon Commission.
(iii) Methods: Indian people organised hartals all over the country. They also held a black flag demonstration with the slogan, “Simon go back”, when the Commission reached Bombay (Mumbai). Such demonstrations were held everywhere it went.
Q.4. List all the different social groups which joined the Non-Cooperation Movement of 1921. Choose any three, and write about their hopes and struggles to show why they joined the movement.
Ans. Social Groups who took part in the NonCooperation Movement. In the Non- Cooperation Movement (1920-1922), the following social groups took part.
(I) Middle-class people in the towns.
The movement in the cities: The Movement started with middle-class participation in the cities. Thousands of students left government-controlled schools and colleges, headmasters and teachers resigned, and lawyers gave up their legal practices.
Boycott of council elections: The Council elections were boycotted in most provinces except Madras (Chennai), where the Justice Party, the party of the nonBrahmans, felt that entering the council was one way of gaining some power, something that usually only Brahmans had an access to.
Swadeshi: The Non-Cooperation Movement had a great impact on the Indian textile industry. Swadeshi goods, especially cloth got a great impetus. Foreign goods were boycotted, liquor shops picketed, and foreign cloth burnt in huge bonfires.
Impact on industry: In many places, merchants and traders refused to trade in foreign goods or finance foreign trade. Due to this, the demand for Indian textile mills and handlooms went up. The increase in demand provided a big relief to the vanishing textile industry of India.
Movement in the countryside: Though people in the countryside interpreted the idea of ‘Swaraj’ in their own way but they participated in the movement on large scale. In Awadh, peasants launched the movement against the talukdars and landlords. Whereas the plantation workers launched the movement against the tea estate owners.
(II) Peasants in rural areas.
(i) Participants: In the countryside, the movement was led by the peasants, tribals and the local leaders. For example, in Awadh, it was Baba Ramchandra sanyasi, who had earlier been to Fiji as an indentured labourer.
(ii) Why rural people participated?
- The movement here was not against the Britishers but against talukdars and landlords. The problems of the rural people were different from those of the urban people:
- The talukdars and landlords were demanding very high rents and a variety of other taxes.
- Peasants had to do begarand work at the landlord’s farms without any payment.
- The peasants had no security of tenure. They were regularly evicted so that they could acquire no security of tenure.
As the problems of the people were different, their demands were also different. The peasant movement demanded:
- Reduction of revenue
- Abolition of begar
- Redistribution of land
- Social boycott of oppressive landlords.
(iii) Ways of protests: The Movement in the countryside had a different angle. In many places, Nai-dhobi bandhs were organised by the Panchayats to deprive the landlords of the services of barbers, cobblers, washermen, etc. Even national leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru went to villages in Awadh to know the grievances of the people. By October, the Awadh Kissan Sabhas was set up headed by Jawaharlal Nehru, Baba Ramchandra, and a few others. When the movement spread in 1921, the houses of talukdars and merchants were attacked. The movement turned violent which was not liked by some of the Congress leaders.
(III) Tribal people.
Most of the tribal people were dependent on forests for their livelihood but under the new Forest Policy, the government had put several restrictions on the people :
- Closing large forest area for the tribal people.
- Forcing the local people to contribute begar.
- Preventing people from entering the forests to graze their cattle, or to collect fuelwood and fruits.
- All these steps enraged the hill people. Not only were their livelihoods affected, but they felt that their traditional rights were also being denied. So the people revolted.
(IV) Plantation workers.
(i) For plantation workers in Assam, freedom meant the right to move freely in and out of the confined space in which they were enclosed, and it meant retaining a link with the village from which they had come.
- The government had passed the Inland Emigration Act of 1859 under which plantation workers were not permitted to leave the tea estates without permission, and in fact, they were rarely given such permission.
- When the plantation workers heard of the Non-Cooperation Movement, thousands of them defied the authorities, left the plantations and headed towards their homes.
- The plantation workers believed that the Gandhi Raj was coming, and everyone would be given land in their own villages.
Q.5. Discuss the Salt March to make clear why it was an effective symbol of resistance against colonialism. [CBSE 2015 (O)]
Ans. The Salt March was an effective symbol of resistance against colonialism because-
- It was the first time that Indian leaders decided to violate law. People were now asked not only to refuse cooperation with the British, but also to break colonial laws.
- Thousands of Indians in different parts of the country broke the salt law, manufactured salt and demonstrated in front of the government salt factories.
- As the movement spread, foreign cloth was boycotted and liquor shops were picketed. Peasants refused to pay revenue and ‘chaukidari taxes’, village officials resigned, and in many places forest people violated forest laws – going into Reserved Forests to collect wood and graze cattle.
- Worried by the development, the colonial government began arresting the Congress leaders, one by one. This led to violent clashes in many places. Angry crowd demonstrated in the streets, facing armoured cars and police firing. Many were killed.
- When Mahatma Gandhi himself was arrested, industrial workers in Sholapur attacked police posts, municipal buildings, law courts and railway stations – all structures that symbolised the British rule.
- The outcome of the movement was the Gandhi-Irwin Pact which was signed by Gandhiji with Irwin on 5th March, 1931. By this Gandhi-Irwin Pact, Gandhiji consented to participate in a Round Table Conference in London and the government agreed to release the political prisoners.
Q.6. Imagine you are a woman participating in the Civil Disobedience Movement. Explain what the experience meant to your life.
Or
‘Women played a very important role in the Civil Disobedience Movement.’ Explain.
Ans.
- Women participated in large numbers in the Civil Disobedience Movement.
- During the movement, thousands of women came out of their homes to listen to Gandhiji.
- They participated in protest marches, manufactured salt, and picked foreign cloth and liquor shops.
- Many were put to jail by the police.
- Moved by Gandhiji’s call, they began to see service to the nation as a sacred duty of women.
Q.7. Why did the political leaders differ sharply over the question of separate electorates ?[CBSE2015]
Ans. By the system of separate electorates, we mean such a system when people of one religion only vote for a candidate of their own religion. Using such a system, was a mischief of the British Government who wanted to divide the people to weaken the national movement. By doing so, the British wanted to prolong their stay in India.
The different political leaders differed over the question of separate electorates because of the following reasons :
(1) The Congress leaders opposed the policy of the British Government in instigating different peoples in demanding separate electorate. They knew well that it was all the mischief of the British Government who encouraged different people to ask for separate electorates because such a policy would weaken the national movement, and prolong Britishers stay in India. The Congress leaders were one and all in favour of joint electorates.
(2) The Muslim leaders, like Muhammed Iqbal and Mr Jinnah asked for separate electorates to safeguard the political interests of the Muslims. In their opinion, the majority of the people were Hindus, and so in case of joint electorates, the Muslims would have little chance of winning the seats. As such, they would always be at the mercy of the Hindus.
(3) The leaders of the Depressed Classes, Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, also asked for separate electorates because in the joint electorates, he feared the dominance of the upper electorates or the upper caste Hindus in the elections. By the Poona Pact he, however, agreed to have joint electorates with the Hindus, provided the seats for the Depressed Classes were fixed or reserved in the Provincial and Central Legislative Councils.
Outcome: Lord Irwin announced in October 1929, a vague, offer of ‘dominion status’ for India.