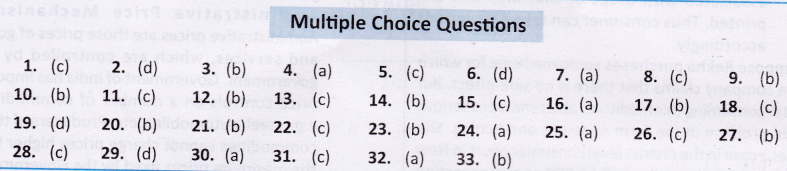
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which one of the following days is being observed as ‘National Consumers Day’
in India?
(a) 24 December
(b) 25 December
(c) 10 December
(d) 31 december
Answer
Answer: (a) 24 December
Question 2.
ISI mark can be seen on which of the following items?
(a) Jewellery
(b) Edible oil
(c) Electrical appliances
(d) Cereals
Answer
Answer: (c) Electrical appliances
Question 3.
‘Hallmark’ is used as a logo for which one of the following?
(a) Agricultural products
(b) Jewellery
(c) Electrical goods
(d) Electronic goods
Answer
Answer: (b) Jewellery
Question 4.
The Consumer Protection Act or COPRA was enacted in the year
(a) 1985
(b) 1986
(c) 1987
(d) 1988
Answer
Answer: (b) 1986
Question 5.
When was the ‘Right to Information’ Act passed?
(a) In January 2002
(b) In March 2004
(c) In October 2005
(d) In July 2007
Answer
Answer: (c) In October 2005
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a right of consumers?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to be informed
(c) Right to choose
(d) Right to constitutional remedies
Answer
Answer: (d) Right to constitutional remedies
Question 7.
When did United Nations adopt the UN Guidelines for Consumer Protection?
(a) 1985
(b) 1990
(c) 1995
(d) 1999
Answer
Answer: (a) 1985
Question 8.
Which of the following is not a function of Consumer Protection Councils?
(a) To create awareness of consumer rights among consumers.
(b) To guide consumers on how to file cases in consumer courts.
(c) To provide compensation to consumers when they are cheated by
shopkeepers.
(d) To represent consumers in Consumer Courts at times.
Answer
Answer: (c) To provide compensation to consumers when they are cheated by shopkeepers.
Question 9.
What was the name given to the agency at the global level for the protection
of consumer rights?
(a) Consumer Court of Justice
(b) International Consumer Forum
(c) Consumers Commission
(d) Consumers International
Answer
Answer: (d) Consumers International
Question 10.
Which one of the following does not provide certificate of standardization in
India?
(a) ISI
(b) Agmark
(c) Hallmark
(d) COPRA
Answer
Answer: (d) COPRA
Question 11.
Suppose you want to buy toothpaste and the shop owner says that he/she can
sell the toothpaste only if you buy a toothbrush, which of your right is being
violated by the shopkeeper?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to be informed
(c) Right to choose
(d) Right to represent
Answer
Answer: (c) Right to choose
Question 12.
Which of the following is not a right of consumers?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to be informed
(c) Right to choose
(d) Right to constitutional remedies
Answer
Answer: (d) Right to constitutional remedies
Question 13.
In October 2005, the Government of India enacted a law known as:
(a) Right to Choose Act
(b) Right to Information Act
(c) Women Reservation Act
(d) Anti-corruption Act
Answer
Answer: (b) Right to Information Act
Question 14.
Which one of the following is not true regarding the Right to Safety?
(a) Right to be protected against unsafe appliances.
(b) Right to protected against unsafe working conditions.
(c) Right to seek information about functioning of government departments.
(d) Right to be protected against services which are hazardous to life.
Answer
Answer: (c) Right to seek information about functioning of government departments.
Question 15.
Which of the following laws was enacted by the Government of India in the year
2005?
(a) The Right to Information Act
(b) The Consumer Protection Act
(c) The Right to Education Act
(d) The Right to Property Act
Answer
Answer: (a) The Right to Information Act
Question 16.
Who amongst the following is protected through rules and regulations in the
market place?
(a) The shopkeepers
(b) The manufactures
(c) The consumers
(d) The suppliers
Answer
Answer: (c) The consumers
Question 17.
Marketing of goods and services which are hazardous to life and property is
covered under:
(a) right to be protected
(b) right to be assured
(c) right to seek redressal
(d) right to be informed
Answer
Answer: (a) right to be protected
Question 18.
Consumer Protection Act, 1986 covers the whole of India except:
(a) the state of Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(c) Lakshadweep
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) the state of Jammu and Kashmir
Question 19.
Who can seek information under the RTI Act, 2005?
(a) A group of persons
(b) An individual citizen
(c) A registered company
(d) An association / society
Answer
Answer: (b) An individual citizen
Question 20.
Consumer Protection Act (COPRA) was enacted by Indian Government in:
(a) 1986
(b) 1983
(c) 1988
(d) 1985
Answer
Answer: (a) 1986
Question 21.
MRP on a product represents:
(a) minimum retail price
(b) maximum retail price
(c) micro retail price
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) maximum retail price
Question 22.
Consumers International was created by:
(a) UNESCO
(b) UN
(c) UNICEF
(d) World Bank
Answer
Answer: (b) UN
Question 23.
Which logo or mark you will have to look for on a biscuit packet?
(a) Agmark
(b) ISI mark
(c) Hallmark
(d) ISO mark
Answer
Answer: (a) Agmark
Question 24.
Factors which cause the exploitation of the consumer:
(a) Limited and wrong information
(b) Illiteracy and ignorance of the consumer
(c) Few sellers and limited competition
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 25.
To protect themselves what do consumers need?
(a) Consumer Forums
(b) Consumer Protection Councils
(c) Consumer movement
(d) Consumer awareness
Answer
Answer: (d) Consumer awareness
Question 26.
Which mark should you look for while buying honey?
(a) ISI
(b) ISO
(c) Agmark
(d) ISO
Answer
Answer: (c) Agmark
Question 27.
Name the court to which a consumer can approach, having a claim of Rs. 40
lakhs
(a) National Consumer Court
(b) State Consumer Court
(c) District Consumer Court
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) State Consumer Court
Question 28.
The organisation which lays down standards of products at the international
level is called:
(a) ISI
(b) ISRO
(c) ISO
(d) WCF
Answer
Answer: (c) ISO
Consumer Rights Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which one of the following logos is used for standardisation of agricultural products? [Delhi, 2012]
(a) I.S.I
(b) Hallmark
(c) Agmark
(d) ISO
2. In which one of the following courts a consumer should file a case if he/she is exploited in the market? [Delhi, 2012]
(a) Local court
(b) State court
(c) Supreme court
(d) Consumer court
3. Hallmark is used as a logo for which one of the following? [AI, 2012]
(a) Agricultural products
(b) Jewellery
(c) Electrical goods
(d) Electronic goods
4. On which one of the following items is I.S.I. used as a logo? [Foreign, 2012]
(a) LPG Cylinder
(b) Jewellery
(c) Gold
(d) Agricultural products
5. For which of these products does it become mandatory for the producer to get certified? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Fruits
(b) Telephones
(c) LPG Cylinders
(d) Cigarettes
6. The district court deals with the cases involving claim up to ………….. [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) ₹ 1 crore
(b) ₹ 40 lakhs
(c) ₹ 30 lakhs
(d) ₹ 20 lakhs
7. The district level consumer court deals with the cares involving claims [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) upto 20 lakhs
(b) upto 15 lakhs
(c) upto 1 crore
(d) upto 25 lakhs
8. Which of the following rights related to availing details of ingredients of a product? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to be informed
(d) Right to represent
9. In which one of the following years was the Right to Information Act Implemented? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) 2004
(b) 2005
(c) 2006
(d) 2007
10. The district level court deals with the cases involving claims: [Delhi 2011]
(a) upto ₹10 lakhs
(b) upto ₹20 lakhs
(c) between ₹20 lakhs to ₹1 crore
(d) exceeding ₹1 crore
11. When did the United Nations adopt the guidelines for consumer protection? [AI 2011]
(a) 1983
(b) 1984
(c) 1985
(d) 1986
12. Which one of the following statements is false? [Foreign 2011]
(a) The consumer has a right to represent in the Consumer Court.
(b) The consumer redressal process is very simple and very quick.
(c) Hallmark is the certification maintained for standardisation of jewellery.
(d) The consumer has the right to be informed.
13. In the market place rules and regulations are required for the protection of the
(a) Sellers
(b) Suppliers
(c) Consumers
(d) Owners
14. In India, the consumer movement as a ……………….. originated with the necessity of protecting and promoting the interests of consumers against unethical and unfair trade practices.
(a) Cultural force
(b) Social force
(c) Economic force
(d) Political force
15. Rampant food shortages, hoarding, black marketing gave birth to the consumer movement in an organized form in the year
(a) 1947s
(b) 1970s
(c) 1960s
(d) 1965s
16. At International level, this has become the foundation for the consumer movement
(a) Consumers International
(b) COPRA
(c) Consumers Forum
(d) None of the above
17. A major step taken in 1986 by the Indian government was the enactment of
(a) RTI Act
(b) Consumer Protection Act.
(c) Consumer Movement
(d) Consumer Courts
18. In case of Reji Mathew, he suffered due to improper anesthesia which resulted in brain abnormalities. Who was held responsible by the National Commission after locking into a complaint ?
(a) Father
(b) Mother
(c) Hospital
(d) Patient himself
19. Because of this right, rules have been made so that the manufacturer displays all the information relating to the commodity
(a) Right to choose
(b) Right to be heard
(c) Right to seek redressal
(d) Right to be informed
20. In October 2005, the Government of India enacted a law known as
(a) Right to Choose Act
(b) Right to Information Act.
(c) COPRA
(d) Public Distribution System
21. A student who has paid lumpsum fee for course of three years to a coaching institute, now decides in between to discontinue that institute due to lack of quality of teaching. Can this student get a proportionate amount of fee refunded as per the law?
(a) No
(b) Yes
(c) May or May Not
(d) None of them
22. Consumers have the right to be protected against any danger caused by goods like electrical goods and pressure cookers. The right referred here is
(a) Right to seek redressal
(b) Right to be heard
(c) Right to safety
(d) Right to consumer education
23. Manufacturer should not use aggressive selling techniques to sell a particular product without giving the consumer a chance to select from alternative products available. Which right is mentioned here?
(a) Right to safety
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to heard
(d) Right to be informed
24. Which right of consumer is violated if the consumers are not allowed to get their claims settled against the manufacturer in case they are cheated or exploited?
(a) Right to seek redressal
(b) Right to choose
(c) Right to be heard
(d) None of them
25. Consumer movement in India has led to the formation of various organizations locally known as
(a) Consumer Protection Council
(b) COPRA
(c) Resident Welfare Association (RWA)
(d) None of them
26. Consumer Forums guide consumers on how to file cases and represent individual consumers in the consumer court. Is this statement true?
(a) No
(b) May or May Not
(c) Yes
(d) Never
27. Under COPRA, a ……………. quasi-judicial machinery was set up for redressal of consumer disputes.
(a) Two-tier
(b) Three-tier
(c) Four-tier
(d) Five-tier
28. State-level court deals with the cases involving claims between
(a) ₹ 1 to 20 lakhs
(b) ₹ 1 Crore and above
(c) ₹ 20 lakhs to ₹ 1 Crore
(d) Any amount
29. Logos and certification which help consumers get assured of quality while purchasing the goods and devices are
(a) ISI
(b) Agmark
(c) Hallmark
(d) All of them
30. National Consumers’ Day in India is observed on
(a) 24 December
(b) 14 December
(c) 14 January
(d) 31 December
31. World Consumers Rights Day is celebrated on
(a) Jan 15
(b) Feb 15
(c) March 15
(d) Jan 1
32. The organization which sets standards of products at the International level
(a) ISO
(b) COPRA
(c) Agmark
(d) BIS
33. Organisation which sets International food standards
(a) Consumer International
(b) Codex Alimentarius Commission
(c) ISO
(d) COPRA
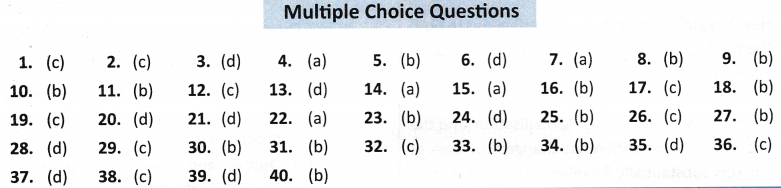
ANSWERS