WELCOME TO PROMISEDPAGE
SMART LEARNING BLOG
HOME
Monday, August 4, 2025
Sunday, September 29, 2024
Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which one of the following organisations lay stress on liberalisation of
foreign trade and foreign investment?
(a) International Monetary Fund
(b) International Labour Organisation
(c) World Health Organisation
(d) World Trade Organisation
Answer
Answer: (d) World Trade Organisation
Question 2.
Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as
(a) Globalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Nationalism
(d) Liberalisation
Answer
Answer: (d) Liberalisation
Question 3.
Which one of the following refers to investment?
(a) The money spent on religious ceremonies
(b) The money spent on social customs
(c) The money spent to buy assets such as land
(d) The money spent on household goods
Answer
Answer: (c) The money spent to buy assets such as land
Question 4.
Which of the following is a ‘barrier’ on foreign trade?
(a) Tax on import
(b) Quality control
(c) Sales tax
(d) Tax on local trade
Answer
Answer: (a) Tax on import
Question 5.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs) are being set up to attract
(a) foreign tourists
(b) foreign investment
(c) foreign goods
(d) foreign policies
Answer
Answer: (b) foreign investment
Question 6.
Entry of MNCs in a domestic market may prove harmful for
(a) all large scale producers
(b) all domestic producers
(c) all substandard domestic producers
(d) all small-scale producers
Answer
Answer: (c) all substandard domestic producers
Question 7.
Ford Motors set up its first plant in India at
(a) Kolkata
(b) Mumbai
(c) Chennai
(d) Delhi
Answer
Answer: (c) Chennai
Question 8.
Which of the following industries have been hard hit by foreign
competition?
(a) Dairy products
(b) Leather industry
(c) Cloth industry
(d) Vehicle industry
Answer
Answer: (a) Dairy products
Question 9.
In which year did the government decide to remove barriers on foreign trade
and investment in India?
(a) 1993
(b) 1992
(c) 1991
(d) 1990
Answer
Answer: (c) 1991
Question 10.
“MNCs keep in mind certain factors before setting up production”. Identify
the incorrect option from the choices given below
(a) Availability of cheap skilled and unskilled labour
(b) Proximity to markets
(c) Presence of a large number of local competitors
(d) Favourable government policies
Answer
Answer: (c) Presence of a large number of local competitors
Question 11.
Why do MNCs set up offices and factories in more than one nation ?
(a) The cost of production is high and the MNCs can earn profit.
(b) The cost of production is low and the MNCs undergoes a loss.
(c) The cost of production is low and the MNCS can earn greater profit.
(d) The MNCs want to make their presence felt globally.
Answer
Answer: (c) The cost of production is low and the MNCS can earn greater profit.
Question 12.
The most common route for investments by MNCs in countries around the world
is to:
(a) set up new factories
(b) buy existing local companies
(c) form partnerships with local companies
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) set up new factories
Question 13.
Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as :
(a) privatisation
(b) globalisation
(c) liberalisation
(d) socialisation
Answer
Answer: (c) liberalisation
Question 14.
Entry of MNCs in a domestic market may prove harmful for:
(a) all large scale producers.
(b) all domestic producers.
(c) all substandard domestic producers.
(d) all small scale producers.
Answer
Answer: (d) all small scale producers.
Question 15.
Which one of the following has benefited least because of globalisation in
India?
(a) Agriculture Sector
(b) Industrial Sector
(c) Service Sector
(d) Secondary Sector
Answer
Answer: (a) Agriculture Sector
Question 16.
Which one of the following is a major benefit of joint production between a
local company and a Multi-National Company?
(a) MNC can bring latest technology in the production
(b) MNC can control the increase in the price
(c) MNC can buy the local company
(d) MNC can sell the products under their brand name
Answer
Answer: (a) MNC can bring latest technology in the production
Question 17.
Which one of the following is not true regarding the World Trade
Organisation?
(a) It allows free trade to all countries without any trade barriers.
(b) Its aim is to liberalise international trade.
(c) It establishes rules regarding internaional trade.
(d) WTO rules have forced the developing countries to remove trade barriers.
Answer
Answer: (a) It allows free trade to all countries without any trade barriers.
Question 18.
Integration of markets means
(a) operating beyond the domestic markets
(b) wider choice of goods
(c) competitive price
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all the above
Question 19.
Which of the following contributes to globalisation?
(a) internal trade
(b) external trade
(c) large scale trade
(d) small scale trade
Answer
Answer: (b) external trade
Question 20.
Investment means spending on
(a) factory building
(b) machines
(c) equipments
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all the above
Question 21.
Multinational corporations have succeeded in entering global markets
through
(a) WTO
(b) UNO
(c) UNESCO
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) WTO
Question 22.
FDI (Foreign Direct Investment) attracted by globalisation in India belongs
to the
(a) World Bank
(b) multinationals
(c) foreign governments
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) multinationals
Question 23.
Which of the following factors has not facilitated globalisation?
(a) Technology
(b) Liberlisation of trade
(c) WTO
(d) Nationalisation of banks
Answer
Answer: (d) Nationalisation of banks
Question 24.
Globalisation so far has been more in favour of:
(a) developed countries
(b) developing countries
(c) poor countries
(d) none of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) developed countries
Question 25.
Cheaper imports, inadequate investment in infrastructure lead to
(a) slowdown in agricultural sector
(b) replace the demand for domestic production
(c) slowdown in industrial sector
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all the above
Question 26.
Which sector has not benefited by the policy of globalisation?
(a) Agricultural sector
(b) Manufacturing sector
(c) Service sector
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Agricultural sector
Question 27.
Fair globalisation refers to ensuring benefits to:
(a) labourers
(b) producers
(c) consumers
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all the above
Globalisation and the Indian Economy Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
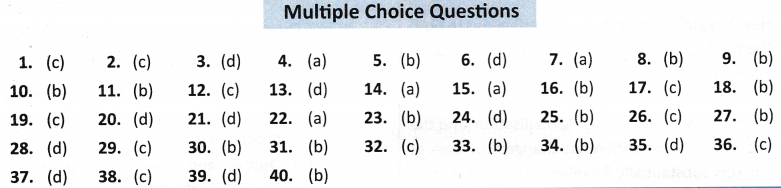
1. Cargill foods is the largest producer of which of the following in India? [Delhi, 2012]
(a) Medicines
(b) Asian Paints
(c) Edible oil
(d) Garments
2. W.T.O. was started at the initiative of which one of the following group of countries? [Delhi, 2012]
(a) Rich countries
(b) Poor countries
(c) Developed countries
(d) Developing countries
3. Which one of the following organisations lays stress on liberalisation of foreign trade and foreign investment? [Delhi, 2012]
(a) International Labour Organisation
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) World Health Organisation
(d) World Trade Organisation
4. Which one of the following is not characteristic of ‘Special Economic Zone’? [AI, 2012]
(a) They do not have to pay taxes for long period.
(b) Government has allowed flexibility in labour laws.
(c) They have world-class facilities.
(d) They do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of five years.
5. Which one of the following Indian industries has been hit hard by globalisation? [AI, 2012]
(a) IT
(b) Toymaking
(c) Jute
(d) Cement
6. Which one of the following type of countries has been more benefited from globalisation? [AI, 2012]
(a) Rich countries
(b) Poor countries
(c) Developing countries
(d) Developed countries
7. Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is called: [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Liberalisation
(b) Investment
(c) Fovourable trade
(d) Free trade
8. Investment made by MNCs are termed as: [CBSE (CCE)2012]
(a) Indigenous investment
(b) Foreign investment
(c) Entrepreneur’s investment
(d) None of the above
9. What is the process of rapid integration or interconnection between countries called? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Industrialization
(b) Globalization
(c) Liberalization
(d) Privatization
10. Which one of the following is an example of a trade barrier? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Tax on Exports
(b) Tax on Imports
(c) Free Trade
(d) Restriction on Export
11. Removal of barriers set by the government is known as [CBSE(CCE)2012]
(a) Globalisation
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Industralisation
(d) Privatisation
12. Globalisation does NOT involve which one of the following? [Delhi 2011]
(a) Rapid integration between countries.
(b) More goods and services moving between countries.
(c) Increased taxes on imports.
(d) Movement of people between countries for jobs, education etc.
13. Which of the following is not a feature of a Multi-National Company? [AI 2011]
(a) It owns/controls production in more than one nation.
(b) It sets up factories where it is close to the markets.
(c) It organises production in complex ways.
(d) It employs labour only from its own country.
14. Liberalisation involves which one of the following? [Foreign 2011]
(a) Removal of trade barriers
(b) Increasing subsidy on fertilisers
(c) Increasing import duties on goods
(d) Increasing export duties on goods
15. The past two decades of globalisation has seen rapid movements in
(a) goods, services and people between countries.
(b) goods, services and investments between countries.
(c) goods, investments and people between countries.
16. The most common route for investments by MNCs in countries around the world is to
(a) set up new factories.
(b) buy existing local companies.
(c) form partnerships with local companies.
17. Globalisation has led to an improvement in living conditions
(a) of all the people
(b) of people in developed countries
(c) of workers in the developing countries
(d) none of the above.
18. Globalisation, by connecting countries, shall result in
(a) lesser competition among producers.
(b) greater competition among producers.
(c) no change in competition among producers.
Additional Questions
19. Company that owns or controls production in more than one nation
(a) Foreign companies
(b) Government companies
(c) Multinational companies
(d) Private companies
20 Investment made by MNCs is called
(a) Mutual investment
(b) Inter-government investment
(c) Portfolio Investment
(d) Foreign investment
21. Benefit to the local company of joint production with MNCs is
(i) Money from MNCs for additional investments
(ii) Moral and Social support
(iii) Latest technology for production
(iv) All of them
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
22. Cargill Foods, a very large American MNC, has bought over smaller Indian companies such as
(a) Parakh Foods
(b) Amul
(c) Britannia
(d) None of the above
23. Cargill is now the largest producer of edible oil in India, with a capacity to make ………… pouches daily.
(a) 6 million
(b) 5 million
(c) 4 million
(d) 55 million
24. Examples of industries where production is carried out by a large number of small producers around the world
(a) Garments
(b) Footwear
(c) Sport items
(d) All of them
25. Ford motors came to India in
(a) 1996
(b) 1995
(c) 1994
(d) 1990
26. Effect of Chinese toys on Indian toymakers is
(a) No effect
(b) Making profits
(c) Suffering losses
(d) None of them
27. Rapid integration or interconnection between countries is known as
(a) Privatisation
(b) Globalisation
(c) Liberalisation
(d) Socialisation
28. Post 50 years have seen several improvements in
(a) Transportation technology
(b) Information technology
(c) Communication technology
(d) All of them
29. Tax on imports is an example of
(a) Terms of Trade
(b) Collateral
(c) Trade Barriers
(d) Foreign Trade
3B Removing barriers or restrictions set by the government is known as
(a) Privatisation
(b) Liberalisation
(c) Globalisation
(d) Socialisation
31. Around which year, need for removing barriers on foreign trade and foreign investment in India was felt ?
(a) 1990
(b) 1991
(c) 1992
(d) 2000
32. ……………. is one such organisation whose aim is to liberalise international trade
(a) UNICEF
(b) World Bank
(c) WTO
(d) IDBI
33. Till 2006, how many members were there in WTO?
(a) 139
(b) 150
(c) 101
(d) 149
34. Companies who set up production units in the Special Economic Zones (SEZs) do not have to pay taxes for an initial period of
(a) 2 years
(b) 5 years
(c) 4 years
(d) 10 years
35. Industries where small manufacturers have been hit hard due to competition.
(a) Batteries
(b) Tyres
(c) Dairy Products
(d) All of them
36. Number of workers that small industries in India employ
(a) 18 million
(b) 19 million
(c) 20 million
(d) 21 million
37. To get large orders, Indian exporters try hard to cut their own costs by
(a) Reducing cost of raw materials
(b) Reducing advertising and marketing cost
(c) Reducing electricity cost
(d) Cutting labour cost
38. To achieve the goal of fair globalisation, a major role can be played by
(i) People
(ii) Government
(iii) MNCs
(iv) None of the above
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
39. It refers to globalisation which creates opportunities for all and ensures that its benefits are better shared.
(a) Privatisation
(b) Special Economic Zones (SEZ)
(c) WTO
(d) Fair globalisation
40. Allowing private sector to set up more and more of such industries as were previously reserved for the public sector.
(a) Globalisation
(b) Privatisation
(c) Liberalisation
(d) Socialisation
ANSWERS
JNV Chapter IV: VMC MCQs Chapter IV: Vidyalaya Management Committee (VMC) - MCQs Test your un...