WELCOME TO PROMISEDPAGE
SMART LEARNING BLOG
HOME
Sunday, August 3, 2025
Sunday, September 29, 2024
Resources and Development Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which of the following methods does not help in soil conservation?
(a) Contour ploughing
(b) Strip cropping
(c) Creating shelter belts
(d) Ploughing up and down the slopes
Answer
Answer: (d) Ploughing up and down the slopes
Question 2.
Which one of the following is a renewable resource?
(a) Coal
(b) Petroleum
(c) Solar energy
(d) Fossil fuels
Answer
Answer: (c) Solar energy
Question 3.
The alluvial soil consists of
(a) sand
(b) silt
(c) clay
(d) all of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all of the above
Question 4.
One of the following which does not check land degradation-
(a) control on overgrazing
(b) creating shelter belts
(c) deforestation
(d) afforestation
Answer
Answer: (c) deforestation
Question 5.
Burial ground is a
(a) community owned resource
(b) national resource
(c) individual resource
(d) international resource
Answer
Answer: (a) community owned resource
Question 6.
Laterite soil is very useful for growing:
(a) Rice, wheat and mustard
(b) Tea, coffee and cashewnut
(c) Pulses, sugarcane and resin
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Tea, coffee and cashewnut
Question 7.
Black soil is deficient in
(a) Calcium carbonate
(b) Magnesium
(c) Potash
(d) Phosphoric contents
Answer
Answer: (d) Phosphoric contents
Question 8.
Which of the following soils has self-aeration capacity?
(a) Alluvial
(b) Red soil
(c) Black soil
(d) Mountain soil
Answer
Answer: (c) Black soil
Question 9.
Ploughing along the contour lines to decelerate the flow of water down the
slopes is called:
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Sheet erosion
(c) Contour ploughing
(d) Terrace cultivation
Answer
Answer: (c) Contour ploughing
Question 10.
Which of the following is not a measure for soil conservation?
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Terrace cultivation
(c) Shelter belts
(d) Overdrawing of ground water
Answer
Answer: (d) Overdrawing of ground water
Question 11.
Resources which are found in a region but have not been utilised are called
(a) developed resources
(b) stock
(c) international resources
(d) potential resources
Answer
Answer: (d) potential resources
Question 12.
Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Extensive cultivation
(b) Deforestation
(c) Overgrazing
(d) Over-irrigation
Answer
Answer: (d) Over-irrigation
Question 13.
Soil formed by intense leaching is:
(a) alluvial soil
(b) red soil
(c) laterite soil
(d) desert soil
Answer
Answer: (c) laterite soil
Question 14.
Which cold desert is relatively isolated from the rest of country?
(a) Leh
(b) Kargil
(c) Ladakh
(d) Dras
Answer
Answer: (c) Ladakh
Question 15.
Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive Cultivation
(b) Overgrazing
(c) Deforestation
(d) Over-irrigation
Answer
Answer: (d) Over-irrigation
Question 16.
What is the percentage share of plains in the total land area?
(a) 43%
(b) 23%
(c) 33%
(d) 27%
Answer
Answer: (a) 43%
Question 17.
Which one of the following states mostly has laterite soil?
(a) Uttar Pradesh
(b) Bihar
(c) Rajasthan
(d) Meghalaya
Answer
Answer: (d) Meghalaya
Question 18.
There is enough for everybody’s need and not for any body’s greed,’’ who among
the following has given the above statement?
(a) Vinoba Bhave
(b) Mahatma Gandhi
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru
(d) Atal Behari Vajpayee
Answer
Answer: (b) Mahatma Gandhi
Question 19.
Which one of the following is a Biotic Resource?
(a) Land
(b) Water
(c) Human beings
(d) Rocks
Answer
Answer: (c) Human beings
Question 20.
Which one of the following is not the community owned resource?
(a) Grazing grounds
(b) Burial grounds
(c) Village ponds
(d) Privately owned house
Answer
Answer: (d) Privately owned house
Question 21.
In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land
degradation?
(a) Jharkhand and Orissa
(b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
Answer
Answer: (b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
Question 22.
How can the resources be classified on the basis of their origin?
(a) Biotic and Abiotic
(b) Renewable and Non-renewable
(c) Individual and Community
(d) Potential and Reserves
Answer
Answer: (a) Biotic and Abiotic
Question 23.
Which one of the following soil is ideal for growing cotton?
(a) Regur Soil
(b) Laterite Soil
(c) Desert Soil
(d) Mountainous Soil
Answer
Answer: (a) Regur Soil
Question 24.
Which among the following is a type of resources classified on the basis of
exhaustibility?
(a) Biotic and abiotic
(b) Renewable and non-renewable
(c) National and individual
(d) Potential and reserves
Answer
Answer: (b) Renewable and non-renewable
Question 25.
What is arrangement of soil in different layers or horizons known as?
(a) Soil Composition
(b) Soil Erosion
(c) Soil Profile
(d) Soil Texture
Answer
Answer: (c) Soil Profile
Resources and Development Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
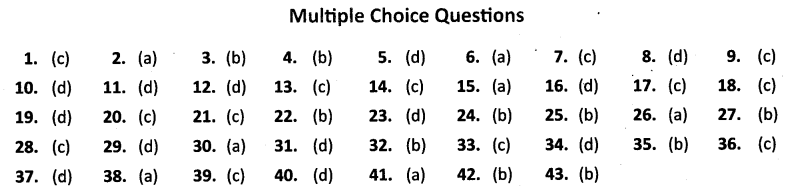
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Resources which are surveyed and their quantity and quality have been determined for utilisation is known as [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Potential resources
(b) Stock
(c) Developed resources
(d) Reserves
2. Which one of the following soil is ideal for growing cotton? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Regur soil
(b) Laterite soil
(c) Desert soil
(d) Mountainous soil
3. In which of the following states is overgrazing responsible for land degradation? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Jharkhand and Orissa
(b) Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Kerala and Tamil Nadu
4. Which one of the following statements is true about the term resources? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Resources are free gifts of nature.
(b) They are the functions of human activities.
(c) All those things which are found in nature.
(d) Things which cannot be used to fulfill our needs.
5. Which one of the following types of the resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable
(b) Biotic
(c) Flow
(d) Non-renewable
6. Under which of the following types of resource the tidal energy can be put?
(a) Replenishable
(b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic
(d) Non-recyclable
7. Soil formed by intense leaching is
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Red soil
(c) Laterite soil
(d) Desert
8. Fallow land refers to
(a) land not under cultivation.
(b) land with many gullies.
(c) a fertile land.
(d) cultivable land not cultivated for a season to regain its fertility.
9. Method of growing long strips of grass between the crops refers to
(a) Contour ploughing
(b) Terrace farming
(c) Strip cropping
(d) Crop rotation
10. Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised.
(a) Renewable
(b) Developed
(c) National
(d) Potential
11. Which of the following factors involves the transformation of things into a resource ?
(i) Physical environment
(ii) Technology
(iii) Human beings
(iv) Institutions
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) All of above
12. Renewable resources are those
(a) which cannot be renewed
(b) which are accessible
(c) which are developed
(d) which are renewed by physical, chemical or mechanical processes.
13. Which one of the following is not a community resource ?
(a) Public parks
(b) A library
(c) A car
(d) A community hall
14. Territorial waters of India extends to
(a) 10 Nautical miles
(b) 15 Nautical miles
(c) 12 Nautical miles
(d) 1900 kilometres
15. Find out which one of the following is a stock?
(a) Biofuels
(b) Coal
(c) Solar energy
(d) Hydro-electricity
16. The first International Earth Summit was held in
(a) Geneva
(b) New York
(c) Japan
(d) Rio de Janeiro
17. “There is enough for everybody’s need but not for anybody’s greed”. Who said this ?
(a) Jawahar Lai Nehru
(b) Atal Bihari Vajpai
(c) M. K. Gandhi
(d) Sunder Lai Bhauguna
18. The area brought under cultivation in a year is called …………….
(a) Fallow land
(b) Cultivable
(c) Net sown area
(d) Gross sown area
19. I am the most widespread soil, covering the Northern Plains and Eastern Coastal Plains-who am I ?
(a) Black soil
(b) Forest soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Alluvial soil
20. Resources which are non-renewable but can be recycled are called
(a) Renewable resources
(b) Non-renewable resources
(c) Recyclable resources
(d) Biotic resources
v21. The most widespread relief feature of India is
(a) Mountains
(b) Forests
(c) Plains
(d) Plateaus
22. The current net sown area of India in 2002-03 is
(a) 45 percent
(b) 43.4 percent
(c) 50 percent
(d) 48 percent
23. The state having maximum net sown area in India is ……………
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Punjab
24. Land left without cultivation for one or less than one agricultural year is called
(a) Culturable waste land
(b) Current fallow land
(c) Waste land
(d) None of the above
25. The present per cent of area under forests is (2002 – 03)
(a) 18 percent
(b) 22.57 percent
(c) 19 percent
(d) 11 percent
26. The factor responsible for maximum land degradation is ………………
(a) Human activities
(b) Wind
(c) Salinity
(d) Soil erosion
27. Which agent is responsible for maximum land degradation ?
(a) Wind
(b) Water
(c) Glaciers
(d) Overgrazing
28. Soil is formed by the process of
(a) Denudation
(b) Gradation
(c) Weathering
(d) Erosion
29. Supply a technical term for the dead and decomposed material found on the top soil.
(a) Bed rock
(b) Fossils
(c) Humidity
(d) Humus
30. The old alluvial soil is known as ………………
(a) Bangar
(b) Bhabbar
(c) Khadar
(d) Regur
31. Which of the following statement(s) is true for black soil ?
(i) It has larger proportion of clay.
(ii) It can retain moisture for a long time.
(iii) It develops cracks during summer which helps in aeration.
(iv) Cotton grows best in this soil.
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) All of the above
32. Red colour of soil is due to
(a) it is rich in humus.
(b) it is rich in iron compounds.
(c) it is derived from volcanic origin.
(d) it is rich in potash.
33. The denudation of the soil cover and washing down of soil by various agents are known as ………………
(a) Weathering
(b) Gradation
(c) Soil erosion
(d) Soil conservation
34. The land consisting of many gullies and ravines are called ……………….
(a) Gully erosion
(b) Bed rock
(c) V shaped valleys
(d) Bad land
35. Terrace cultivation can be used to control soil erosion in
(a) Desert regions
(b) Hill slopes
(c) Valleys
(d) Plains
36.Strip cropping refers to
(a) growing of crops in long strips.
(b) growing of trees in long rows.
(c) growing of strips of grass in between the crops.
(d) ploughing along the contour lines.
37. Erosion of the top soil when water flows as a sheet over large areas down the slope is called
(a) Gully erosion
(b) Badlands
(c) Soil erosion
(d) Sheet erosion
38. Which one of the following statements is correct as regards to international resources ?
(a) Resources which are regulated by international institutions.
(b) Resources which lie beyond the territorial waters.
(c) Resources which are found along the international frontier.
(d) Resources which are not yet developed.
39. Which one of the following methods is ideal for controlling land degradation in coastal areas and in deserts ?
(a) Strip cropping
(b) Contour ploughing
(c) Planting of shelter belts
(d) Plugging of gullies
40. Which type of soil is suitable for the growth of cashew nut ?
(a) Alluvial soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Red soil
(d) Red laterite soil
41. Arid soils are less fertile as
(i) it lacks humus and moisture
(ii) it has high salt content
(iii) it is sandy in nature
(iv) it is rich in Iron
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
42. Ploughing along the contour lines can
(a) accelerate the flow of water.
(b) decelerate the flow of water.
(c) accelerate the force of winds.
(d) decelerate the force of winds.
43. Bad lands or ravines are found in
(a) Chenab basin
(b) Chambal basin
(c) Ganga basin
(d) Godavari basin
ANSWERS
JNV Chapter IV: VMC MCQs Chapter IV: Vidyalaya Management Committee (VMC) - MCQs Test your un...