WELCOME TO PROMISEDPAGE
SMART LEARNING BLOG
HOME
Sunday, August 3, 2025
Outcomes of Democracy
Saturday, September 28, 2024
Outcomes of Democracy Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which one of the following is an example of outcomes of a democracy that
produces an accountable government?
(a) Open to public debates on major policies and legislation
(b) Open in promoting economic development
(c) Open in reducing economic inequalities
(d) Open to rulers elected by the people
Answer
Answer: (a) Open to public debates on major policies and legislation
Question 2.
Which one of the following is the most popular form of government in the
contemporary world?
(a) Dictatorship
(b) Monarchy
(c) Military rule
(d) Democracy
Answer
Answer: (d) Democracy
Question 3.
Which one of the following features is common to most of the democracies?
(a) They have formal Constitution
(b) They hold regular elections
(c) They have political parties
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Question 4.
In which one of the following countries is democracy not preferred over
dictatorship?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Pakistan
(c) Sri Lanka
(d) India
Answer
Answer: (b) Pakistan
Question 5. Which one of the following is not the way to resolve a conflict in a democracy?
(a) Mass mobilisation
(b) Using Parliament
(c) Doing justice
(d) Armed revolution
Answer
Answer: (d) Armed revolution
Question 6.
‘Equal treatment of women’ is a necessary ingredient of a democratic society.
This means that:
(a) women are actually always treated with respect.
(b) it is now easier for women to legally wage struggle for their rights.
(c) most societies across the world are now increasingly women dominated.
(d) women are now treated as equals in the political arena.
Answer
Answer: (b) it is now easier for women to legally wage struggle for their rights.
Question 7.
Democratic government is better than non-democratic because
(a) it is a legitimate form of government.
(b) overwhelming support for the idea all over the world.
(c) it leads to a just distribution of goods and opportunities.
(d) it ensures faster economic growth.
Answer
Answer: (a) it is a legitimate form of government.
Question 8.
Consider the following statements. Which of these do not hold true for
non-democratic regimes?
(a) These do not have to bother about public opinion.
(b) These take less time at arriving at a decision.
(c) Principle of individual dignity has legal force.
(d) These often suppress internal social differences.
Answer
Answer: (c) Principle of individual dignity has legal force.
Question 9.
In a democracy, a citizen has the right and means to examine the process of
decision¬making. This is known as
(a) Dictatorship
(b) Transparency
(c) Legitimacy
(d) Equality
Answer
Answer: (b) Transparency
Question 10.
To measure democracies on the basis of expected outcomes, which of the
following practices and institutions would one look for?
(a) Regular, free and fair elections
(b) Open public debate on major policies
(c) Citizens’ right to information about the government
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Question 11.
On which of the following practices and institutions can the accountability of
government and involvement of people in decision-making process in a democracy
be measured?
(a) Regular, free and fair elections
(b) Public debate on major policies and legislations
(c) Citizens’ right to information about government and its functioning
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above
Question 12.
Decisions taken by which type of government are likely to be more acceptable
to the people and more effective?
(a) Democratic government
(b) Non-democratic government
(c) Military dictatorship
(d) Theocracy
Answer
Answer: (a) Democratic government
Question 13.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Democracies can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different
groups
(b) Dictatorships can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different
groups
(c) No regime can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different
groups
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (c) No regime can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different groups
Question 14.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Most of the democracies have constitutions, they hold elections, have
parties and they guarantee rights to citizens
(b) Democracies are very much different from each other in terms of their
social, economic and cultural achievements
(c) All democracies are similar as far as social, economic and cultural
conditions are concerned
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (d) Both (a) and (b)
Question 15.
Why is there a delay in decision-making and implementation in a democracy?
(a) The government don’t want to take decisions
(b) The government is hesitant in taking decisions
(c) Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation
(d) A democratic government is not interested in taking quick decisions
Answer
Answer: (c) Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation
Question 16.
In the context of democracies, what is successfully done by Democracies?
(a) Eliminated conflicts among people
(b) Eliminated economic inequalities among people
(c) Eliminated differences of opinion about how marginalised sections are to
be treated
(d) Rejected the idea of political inequality
Answer
Answer: (d) Rejected the idea of political inequality
Question 17.
What is promoted much superiorly by democracy than any other form of
government?
(a) Economic growth
(b) Dignity and freedom of the individual
(c) Economic equality
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Dignity and freedom of the individual
Question 18.
Which regimes often turn a blind eye to or suppress internal social
differences?
(a) Democratic regimes
(b) Non-democratic regimes
(c) Monarchy
(d) Oligarchy
Answer
Answer: (b) Non-democratic regimes
Question 19.
In which of these countries half of the population lives in poverty?
(a) India
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Pakistan
Answer
Answer: (c) Bangladesh
Question 20.
Which among the following has a higher rate of economic growth and
development?
(a) Democracies
(b) Dictatorships
(c) All non-democratic regimes
(d) Monarchies
Answer
Answer: (b) Dictatorships
Picture-based Questions:
Question 1.
Look at the given cartoons taken from NCERT Textbook pages 93-96 and 99.
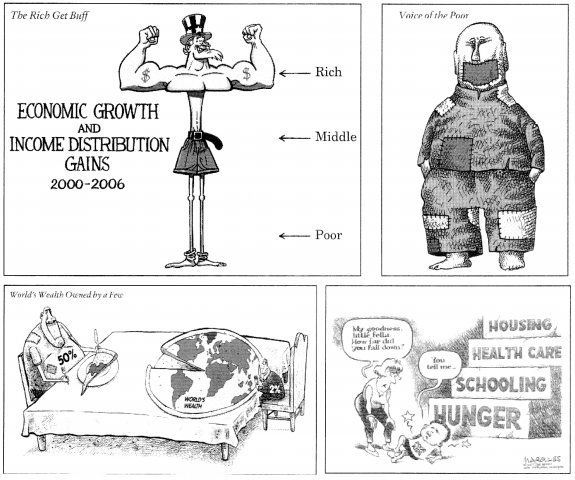
The above cartoons tell us about the disparities between the rich and the
poor. Should the gains of economic growth be evenly distributed? How can the
poor get a voice for a better share in a nation? What can the poor countries
do to receive a greater share in the world’s wealth?
Answer
Answer:
In democracy all over the world we find disparities between the rich and the
poor. The reason is that the gains of economic growth is not evenly
distributed among the people. A smaller number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly
disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. But those at the bottom of the
society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining.
Sometimes they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as
food, clothing, house, education and health.
To get a voice for a better share in a nation the poor need to come together and draw government’s attention towards their problems. If needed, they should start protest movements to get coverage in media.
The poor countries should get united and raise their voice collectively to draw the attention of the rich and powerful countries towards the problems they are suffering from. They should point out how rich countries are accountable to some of their problems and how they exploit natural resources so carelessly. The poor countries should hold meetings and discussions to pressurise the rich countries to stop doing injustices.
Outcomes of Democracy Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
I. Introduction (MCQ 1 to 10) – Outcomes of Democracy MCQ
Question 1: What is one of the key features of democracy?
A. Centralized power
B. Rule by monarchy
C. Promotion of equality among citizens
D. Military rule
Answer: C. Promotion of equality among citizens. Democracy promotes equality among its citizens.
Question 2: How does democracy improve decision-making?
A. By quick decisions without deliberation
B. By allowing dictators to make decisions
C. Through deliberation and debate
D. By ignoring the opinions of the masses
Answer: C. Through deliberation and debate. Democracy emphasizes careful decision-making through public discussion.
Question 3: Which of the following is NOT an expectation from democracy?
A. Equality among citizens
B. Freedom to correct mistakes
C. Swift and autocratic decisions
D. Dignity of the individual
Answer: C. Swift and autocratic decisions. Democracy encourages careful and inclusive decision-making processes.
Question 4: How does democracy ensure the dignity of individuals?
A. By promoting economic development
B. By allowing freedom of speech and participation
C. By restricting social mobility
D. By increasing government control over individuals
Answer: B. By allowing freedom of speech and participation. Democracy ensures individuals’ dignity by granting them rights and participation in governance.
Question 5: What dilemma do people face when assessing democracy?
A. Democracy is good in principle but disappointing in practice
B. Democracy allows rulers to ignore public opinion
C. Democracy focuses only on economic outcomes
D. Democracy creates more conflicts than other forms of government
Answer: A. Democracy is good in principle but disappointing in practice. People often support democracy ideologically but are frustrated with its implementation.
Question 6: How does democracy provide a method to resolve conflicts?
A. By allowing leaders to make decisions without consulting the people
B. By enabling open discussion and deliberation
C. By suppressing public opinions
D. By enforcing strict rules without debate
Answer: B. By enabling open discussion and deliberation. Democracy encourages dialogue and debate to peacefully resolve conflicts.
Question 7: Which of the following is NOT an outcome that democracies generally promote?
A. Enhancing individual dignity
B. Promoting political equality
C. Eliminating decision-making processes
D. Allowing room to correct mistakes
Answer: C. Eliminating decision-making processes. Democracies actually improve decision-making through careful deliberation and public input.
Question 8: What is the most fundamental expectation people have from democracy?
A. Fast and undebated decision-making
B. A government that represents and is accountable to the people
C. Strict laws that cannot be challenged
D. Complete elimination of poverty
Answer: B. A government that represents and is accountable to the people. A key expectation from democracy is that the government should be accountable to its citizens.
Question 9: How do citizens generally view democracy in comparison to other forms of government?
A. Democracy is slower but more inclusive
B. Democracy is quicker in decision-making
C. Democracy completely eliminates all social inequalities
D. Democracy is unpopular and ineffective
Answer: A. Democracy is slower but more inclusive. Though democracy can be slower due to deliberation, it is more inclusive and allows public participation.
Question 10: Why do people face a dilemma when evaluating democracy?
A. Democracy promotes authoritarianism
B. Democracy is good in principle but often lacks in practice
C. Democracy eliminates all social conflicts
D. Democracy provides no room for improvement
Answer: B. Democracy is good in principle but often lacks in practice. While democracy is valued for its ideals, its practical implementation can sometimes fall short.
Question 11: What is one common expectation of democratic governments?
A. The elimination of political parties
B. Reduction in conflicts
C. Quick decision-making without consultation
D. Unequal distribution of resources
Answer: B. Reduction in conflicts. Democracy is expected to provide methods for resolving conflicts peacefully.
Question 12: In what way does democracy fall short in practice?
A. It eliminates inequality
B. It always provides effective government
C. It sometimes fails to meet citizens’ expectations
D. It ensures corruption-free governance
Answer: C. It sometimes fails to meet citizens’ expectations. Democracy often does not fully deliver on its promises.
Question 13: Why do people continue to support democracy despite its flaws?
A. It allows for economic growth
B. It promotes public debate and accountability
C. It requires less citizen involvement
D. It is free from delays in decision-making
Answer: B. It promotes public debate and accountability. People value democracy’s mechanisms for holding governments accountable.
Question 14: How can we assess the effectiveness of a democracy?
A. By its ability to provide quick solutions to problems
B. By the freedom of its citizens to criticize the government
C. By the size of its economy
D. By the number of political parties
Answer: B. By the freedom of its citizens to criticize the government. A key measure of democracy’s success is the ability of citizens to hold the government accountable.
Question 15: Which of the following is an example of a democratic failure?
A. Equal treatment of all citizens
B. Effective resolution of conflicts
C. Slow decision-making with extensive debate
D. Ignoring the needs of the majority
Answer: D. Ignoring the needs of the majority. Democracies can sometimes fail to address the needs of the majority population.
Question 16: What causes frustration with democracy among citizens?
A. Lack of elections
B. Slow decision-making process
C. Frequent public debates
D. Excessive government transparency
Answer: B. Slow decision-making process. The deliberative nature of democracy often causes delays in decision-making, leading to frustration.
Question 17: What is an advantage of democracy despite its slow processes?
A. Decisions are more likely to be accepted by the people
B. It eliminates the need for public opinion
C. It allows for more authoritarian control
D. Citizens are excluded from decision-making
Answer: A. Decisions are more likely to be accepted by the people. Democracy’s deliberative process results in decisions that are more widely accepted.
Question 18: Why do democracies often face criticism despite holding elections?
A. Elections are infrequent and unfair
B. They fail to involve citizens in decision-making
C. They do not ensure public debate
D. Citizens feel elections alone are not enough to solve problems
Answer: D. Citizens feel elections alone are not enough to solve problems. While elections are important, they do not guarantee that other aspects of democracy are functioning well.
Question 19: What is a common problem that democracies struggle to address effectively?
A. Equal rights for citizens
B. Freedom of speech
C. Economic inequality
D. Holding elections
Answer: C. Economic inequality. Despite political equality, democracies often struggle to address economic disparities.
Question 20: What is the core challenge that democracies face in practice?
A. Balancing public accountability with effective governance
B. Preventing public debate
C. Restricting political participation
D. Increasing government secrecy
Answer: A. Balancing public accountability with effective governance. Democracies aim to maintain transparency and accountability, but this can sometimes hinder swift action.
Question 21: What is a common expectation from democracy regarding governance?
A. Autocratic decision-making
B. Corruption-free government
C. Minimal citizen involvement
D. Frequent elections without public input
Answer: B. Corruption-free government. People often expect democratic governments to be less corrupt and more transparent.
Question 22: What do people often expect democracy to improve?
A. Social conflict
B. Public debate
C. Economic disparities
D. Freedom of speech
Answer: C. Economic disparities. There is often an expectation that democracy will lead to the reduction of economic inequalities.
Question 23: What can be a potential weakness in democracies compared to other forms of government?
A. High public participation
B. Slower decision-making process
C. Transparency in governance
D. More public debate
Answer: B. Slower decision-making process. The deliberative nature of democratic governance often leads to delays in decision-making.
Question 24: What is one reason democracies may fall short of economic expectations?
A. Over-reliance on global markets
B. Too much political stability
C. Failure to eliminate inequality
D. Frequent changes in government
Answer: C. Failure to eliminate inequality. Democracies are often criticized for not adequately addressing economic inequalities.
Question 25: What is an essential aspect of democracy that helps to manage public dissatisfaction?
A. Secret decision-making processes
B. Opportunities for public debate and expression of grievances
C. Limiting citizen involvement in politics
D. Ensuring government inefficiency
Answer: B. Opportunities for public debate and expression of grievances. Democracy allows citizens to express dissatisfaction, which can be an indicator of its success.
III. Accountable, Responsive, and Legitimate Government (MCQ 26 to 45)
Question 26: What is the most basic outcome that democracy must provide?
A. Government control over all decisions
B. Quick and secret decision-making
C. Accountability of the government to its citizens
D. The elimination of public debates
Answer: C. Accountability of the government to its citizens. A core democratic principle is the government’s accountability to the people.
Question 27: How do democratic governments ensure accountability?
A. By excluding citizens from decision-making
B. By holding regular and free elections
C. By restricting public debates
D. By eliminating opposition parties
Answer: B. By holding regular and free elections. Elections ensure that citizens can hold their rulers accountable.
Question 28: What is one criticism of democratic governments in terms of efficiency?
A. They make decisions too quickly
B. They are less efficient due to deliberation
C. They exclude the public from decisions
D. They are secretive about processes
Answer: B. They are less efficient due to deliberation. Democratic governments may be slower due to the need for discussion and negotiation.
Question 29: Why might democratic governments take longer to make decisions?
A. They avoid public opinion
B. They prioritize quick decisions
C. They emphasize deliberation and negotiation
D. They have fewer checks and balances
Answer: C. They emphasize deliberation and negotiation. Democratic decision-making often involves discussion and compromise, which takes time.
Question 30: What does the transparency in democratic governments ensure?
A. That decisions are made in secretv B. That citizens can monitor decision-making processes
C. That government actions are hidden from public view
D. That leaders can make decisions without public input
Answer: B. That citizens can monitor decision-making processes. Transparency allows citizens to see how decisions are made and hold the government accountable.
Question 31: What is the primary benefit of democratic decision-making, even though it takes more time?
A. Faster results
B. Decisions are more acceptable to the people
C. Exclusion of public opinions
D. Elimination of public debate
Answer: B. Decisions are more acceptable to the people. The deliberation process ensures that decisions made in a democracy have broader public acceptance.
Question 32: How does democracy ensure that decisions are transparent?
A. By allowing rulers to make decisions without consultation
B. By excluding citizens from decision-making
C. By following procedures that can be monitored by the public
D. By making decisions in secret
Answer: C. By following procedures that can be monitored by the public. Transparency ensures citizens can see how decisions are made and hold the government accountable.
Question 33: What do democratic governments rely on to maintain accountability?
A. Military control
B. Public support and participation
C. Quick, undebated decision-making
D. Unfair election practices
Answer: B. Public support and participation. Democracies rely on public involvement in decision-making and accountability mechanisms.
Question 34: How does democracy compare to non-democratic regimes in terms of transparency?
A. Democracy offers less transparency
B. Democracy provides more transparency
C. Both are equally transparent
D. Non-democratic regimes are more transparent
Answer: B. Democracy provides more transparency. Democratic governments generally offer more opportunities for public scrutiny of decision-making.
Question 35: What ensures that democratic governments remain accountable to the people?
A. Decisions made in secrecy
B. Citizens’ ability to participate in decision-making
C. Restricting public involvement
D. Limiting public debates
Answer: B. Citizens’ ability to participate in decision-making. Participation in decision-making processes ensures governments remain accountable.
Question 36: Which of the following is a key democratic principle?
A. Centralized decision-making
B. Citizens have no right to information
C. Citizens can hold the government accountable
D. Governments are not bound to public opinion
Answer: C. Citizens can hold the government accountable. Accountability is a central principle in democratic governance.
Question 37: How do democracies deal with criticism about inefficiency?
A. By excluding public opinion
B. By explaining that deliberation leads to more acceptable decisions
C. By avoiding public debates
D. By making all decisions secret
Answer: B. By explaining that deliberation leads to more acceptable decisions. Democracies argue that the time taken in decision-making ensures broader public acceptance.
Question 38: Why are democratic governments often considered legitimate?
A. They make decisions without public input
B. They allow for public participation and elections
C. They ignore the majority opinion
D. They restrict public access to information
Answer: B. They allow for public participation and elections. Democracies are considered legitimate because they are based on public participation and fair elections.
Question 39: What can citizens expect from a well-functioning democracy?
A. Secret decision-making
B. The ability to monitor and influence governmental actions
C. Exclusion from governmental decisions
D. A focus on efficiency over public opinion
Answer: B. The ability to monitor and influence governmental actions. Democracy ensures that citizens have mechanisms to hold their government accountable.
Question 40: Why is the support for democracy strong worldwide, despite its inefficiencies?
A. Democracy allows rulers to remain unaccountable
B. Democracy is seen as legitimate and represents people’s own government
C. People prefer centralized and quick decision-making
D. Non-democracies are seen as equally legitimate
Answer: B. Democracy is seen as legitimate and represents people’s own government. People support democracy because they feel it is a government that is accountable to them.
Question 41: How does democracy ensure responsiveness to the people’s needs?
A. By allowing rulers to govern without input
B. Through mechanisms like elections and public debate
C. By restricting the right to information
D. By making decisions in secret
Answer: B. Through mechanisms like elections and public debate. Democracies ensure responsiveness through public participation and feedback.
Question 42: What is one way that democracy prevents corruption?
A. By allowing decisions to be made in secret
B. Through transparency and accountability measures
C. By ignoring public opinions
D. By restricting public participation in government
Answer: B. Through transparency and accountability measures. Democracy encourages transparency, which helps to reduce corruption.
Question 43: How do non-democratic regimes differ from democracies in decision-making? A. Non-democracies prioritize deliberation
B. Democracies make decisions without public input
C. Non-democracies make quicker decisions without consulting the public
D. Democracies avoid involving citizens in the decision-making process
Answer: C. Non-democracies make quicker decisions without consulting the public. Non-democratic regimes tend to make decisions more quickly because they don’t involve public deliberation.
Question 44: Why are democracies preferred over non-democratic regimes despite some inefficiencies?
A. They provide faster solutions
B. They are seen as legitimate and accountable to the people
C. They restrict public debates
D. They do not involve elections
Answer: B. They are seen as legitimate and accountable to the people. Despite inefficiencies, democracy’s legitimacy and accountability are key reasons for its preference.
Question 45: What is one common outcome of democracy that people value?
A. Freedom from public debate
B. Control of decisions by a few
C. Freedom to criticize and hold the government accountable
D. The exclusion of citizens from decision-making
Answer: C. Freedom to criticize and hold the government accountable. Democracies allow citizens the freedom to hold their government accountable and express their opinions.
IV. Economic Growth and Development (MCQ 46 to 60)
Question 46: What is a common expectation from democracy in terms of economic performance?
A. Rapid economic growth
B. Elimination of public debate
C. Increased economic development
D. Complete equality of income
Answer: C. Increased economic development. People expect democratic governments to promote economic growth and development.
Question 47: How do democracies generally perform in terms of economic growth compared to dictatorships?
A. Democracies always have higher growth
B. Democracies and dictatorships show similar growth rates
C. Dictatorships consistently outperform democracies
D. Economic growth is unrelated to political systems
Answer: B. Democracies and dictatorships show similar growth rates. Studies indicate that both forms of governance achieve similar rates of economic growth over time.
Question 48: Why is it challenging to assess democracy based purely on economic growth?
A. Democracy always leads to economic failure
B. Economic growth depends on various factors beyond the political system
C. Dictatorships are always better for economic growth
D. Economic development only occurs under democratic regimes
Answer: B. Economic growth depends on various factors beyond the political system. Factors like population, global situation, and national policies affect economic growth, making it difficult to attribute growth solely to the political system.
Question 49: What is one key factor that influences a country’s economic development, regardless of its political system?
A. Speed of decision-making
B. The global economic situation
C. The number of political parties
D. Exclusion of citizens from governance
Answer: B. The global economic situation. External factors, such as global markets and international relations, significantly affect a country’s economic development.
Question 50: What is one economic expectation that democracy might fail to meet?
A. Elimination of public debate
B. Rapid economic development
C. Reduction in corruption
D. Improvement in literacy rates
Answer: B. Rapid economic development. While democracies aim for economic development, they sometimes struggle to achieve rapid growth.
Question 51: How does democracy compare to dictatorship regarding economic development in poor countries?
A. Democracies significantly outperform dictatorships
B. Dictatorships perform slightly better
C. There is little difference in economic growth rates
D. Democracies have consistently failed to promote growth
Answer: C. There is little difference in economic growth rates. In poor countries, the economic performance of democracies and dictatorships is nearly the same.
Question 52: Why might democracies be preferred over dictatorships despite similar economic growth rates?
A. Democracies promote human rights and accountability
B. Democracies eliminate all forms of inequality
C. Dictatorships are known for corruption
D. Democracies suppress public opinion
Answer: A. Democracies promote human rights and accountability. Democracies are often preferred because they offer more rights, transparency, and accountability.
Question 53: How do political systems impact economic inequalities?
A. Democracies always eliminate inequalities
B. Democracies often struggle with high economic inequality
C. Dictatorships prevent economic disparities
D. Economic inequalities are not influenced by the political system
Answer: B. Democracies often struggle with high economic inequality. Although political equality is a cornerstone of democracy, economic inequalities often persist.
Question 54: In which of the following aspects do democracies and dictatorships show the most similarity?
A. Rate of economic development in poor countries
B. Public accountability
C. Degree of public participation
D. Respect for human rights
Answer: A. Rate of economic development in poor countries. Both systems tend to show similar levels of economic development in poorer nations.
Question 55: Which factor often influences the economic performance of democratic countries?
A. Lack of elections
B. Deliberation and negotiation
C. Exclusion of public debates
D. Global cooperation and economic policies
Answer: D. Global cooperation and economic policies. External economic factors and international cooperation play a key role in determining the economic outcomes of democratic nations.
Question 56: What do democracies offer beyond just economic development?
A. Increased secrecy in governance
B. Public participation, human rights, and transparency
C. Elimination of global dependencies
D. Complete economic equality
Answer: B. Public participation, human rights, and transparency. Democracies provide benefits such as accountability, citizen involvement, and protection of individual freedoms.
Question 57: How does democracy perform in terms of economic development when compared to dictatorships?
A. Democracies significantly outperform dictatorships
B. Dictatorships show a slightly higher growth rate
C. Democracies eliminate poverty more effectively
D. Economic growth is the same for both systems
Answer: B. Dictatorships show a slightly higher growth rate. Historically, some data shows that dictatorships have a marginally higher growth rate compared to democracies.
Question 58: Why might economic performance alone not be the best measure of a government’s success?
A. Political participation is not relevant
B. Economic development is unrelated to citizen welfare
C. Factors like accountability, freedom, and human rights matter
D. Governments should focus solely on economic output
Answer: C. Factors like accountability, freedom, and human rights matter. Successful governance includes not just economic performance but also respect for rights and citizen involvement.
Question 59: How can democracy indirectly contribute to economic growth?
A. By centralizing decision-making
B. By fostering cooperation and long-term policies
C. By eliminating public opinion
D. By excluding minorities from governance
Answer: B. By fostering cooperation and long-term policies. Democracies often encourage collaboration and stable policy-making, which can promote sustained economic development.
Question 60: What expectation do people often have from democracy regarding economic growth?
A. That it should be faster than dictatorships
B. That it should guarantee complete economic equality
C. That it will not lag behind non-democracies
D. That it should exclude public debates to speed up growth
Answer: C. That it will not lag behind non-democracies. People expect democracy to at least match, if not exceed, the economic performance of non-democratic regimes.
Question 61: What is a common expectation from democracies in terms of economic inequality?
A. Complete elimination of inequality
B. Increase in economic disparities
C. Reduction of inequality and poverty
D. Ignoring economic inequality
Answer: C. Reduction of inequality and poverty. People expect democracies to address economic disparities and reduce poverty.
Question 62: Why is it challenging for democracies to reduce economic inequality?
A. They do not have the resources to address inequality
B. Democracies prioritize economic growth over equality
C. Inequality is deeply embedded in society
D. Public participation hinders decision-making
Answer: C. Inequality is deeply embedded in society. Addressing deep-rooted economic disparities is a complex challenge for democracies.
Question 63: What is the relationship between political and economic equality in democracies?
A. Democracies ensure both types of equality
B. Political equality exists, but economic inequality often persists
C. Democracies ignore both political and economic equality
D. Democracies ensure economic equality but not political equality
Answer: B. Political equality exists, but economic inequality often persists. While democracies provide political equality, economic inequalities remain significant.
Question 64: What is the paradox of poverty in democratic nations?
A. Democracies are better at eliminating poverty
B. Poor voters often support the party that ignores their needs
C. Democracies are ineffective in addressing poverty
D. Poverty does not exist in democracies
Answer: B. Poor voters often support the party that ignores their needs. Despite being the majority, the poor often do not see their concerns fully addressed in democracies.
Question 65: How do democratic governments typically respond to economic inequality?
A. By ignoring the issue
B. By instituting policies to address disparities
C. By eliminating economic growth
D. By increasing taxes for the rich
Answer: B. By instituting policies to address disparities. Democratic governments often implement policies aimed at reducing economic inequality.
Question 66: Why do democracies sometimes struggle to reduce poverty effectively?
A. Lack of elections
B. Economic priorities that do not focus on poverty reduction
C. Complete elimination of public participation
D. Rapid economic development without concern for inequality
Answer: B. Economic priorities that do not focus on poverty reduction. Democracies sometimes prioritize other areas, such as infrastructure, over direct poverty alleviation.
Question 67: Which of the following is a key challenge for democracies in addressing economic disparities?
A. A lack of political stability
B. The persistence of wealth concentration among the elite
C. Too much involvement of citizens in decision-making
D. Complete elimination of poverty
Answer: B. The persistence of wealth concentration among the elite. In many democracies, wealth remains concentrated in the hands of a small, privileged group.
Question 68: What expectation do citizens often have from democratically elected governments in terms of inequality?
A. That they will eliminate all forms of inequality
B. That they will increase economic disparities
C. That they will implement policies to reduce poverty and inequality
D. That they will ignore poverty and focus on economic growth
Answer: C. That they will implement policies to reduce poverty and inequality. Citizens expect democratically elected governments to address economic disparities and improve the lives of the poor.
Question 69: How do economic inequalities manifest in democratic countries?
A. Complete elimination of poverty
B. Growing disparities between the rich and the poor
C. Equal distribution of wealth among citizens
D. Absence of income inequality
Answer: B. Growing disparities between the rich and the poor. Despite democratic ideals of equality, economic disparities often grow in many democracies.
Question 70: What is the role of democratic governance in reducing poverty?
A. Ignoring the needs of the poor
B. Ensuring that wealth is concentrated among the elite
C. Providing equal opportunities and access to resources for all citizens
D. Limiting public participation in economic decisions
Answer: C. Providing equal opportunities and access to resources for all citizens. Democratic governments are expected to create policies that give citizens equal access to resources and opportunities.
VI. Accommodation of Social Diversity (MCQ 71 to 85) Question
71: What is a core expectation of democracies in terms of social diversity?
A. That they eliminate all social differences
B. That they allow for peaceful coexistence and respect for differences
C. That they ignore the demands of minority groups
D. That they enforce uniformity among citizens
Answer: B. That they allow for peaceful coexistence and respect for differences. Democracies are expected to accommodate and respect various social, ethnic, and cultural differences.
Question 72: Why is it important for democracies to accommodate social diversity?
A. To prevent conflicts and promote social harmony
B. To increase economic growth
C. To limit citizen participation
D. To enforce a single cultural identity
Answer: A. To prevent conflicts and promote social harmony. Accommodating social diversity helps democracies prevent conflicts and ensure peaceful coexistence.
Question 73: How do democracies typically manage social divisions?
A. By suppressing minority groups
B. By enforcing a uniform national identity
C. Through negotiation and peaceful conflict resolution
D. By ignoring social differences
Answer: C. Through negotiation and peaceful conflict resolution. Democracies work to manage social divisions through discussion and peaceful resolution.
Question 74: What is a key condition for achieving social harmony in a democracy?
A. Exclusion of minority groups from decision-making
B. The majority working with the minority to represent general views
C. The dominance of one cultural or ethnic group
D. Complete elimination of elections
Answer: B. The majority working with the minority to represent general views. Democracy requires cooperation between majority and minority groups to ensure inclusive governance.
Question 75: What does “rule by majority” mean in a democratic context?
A. Only the majority group can make decisions
B. The majority permanently excludes minority opinions
C. The majority must work with the minority to create inclusive policies
D. The majority always holds power
Answer: C. The majority must work with the minority to create inclusive policies. In a democracy, the majority should collaborate with the minority to ensure all voices are heard.
Question 76: What risk does a democracy face if the majority dominates in terms of religion or race?
A. Increased transparency in governance
B. Greater social harmony
C. Rule by a single group, leading to exclusion of others
D. Enhanced public participation
Answer: C. Rule by a single group, leading to exclusion of others. When majority rule is based on race, religion, or ethnicity, it risks marginalizing minority groups and undermining democracy.
Question 77: What outcome should a well-functioning democracy produce in terms of social diversity?
A. Suppression of minority opinions
B. Creation of opportunities for all citizens to be part of the majority at some point
C. Permanent exclusion of certain groups from governance
D. Elimination of public debate on social differences
Answer: B. Creation of opportunities for all citizens to be part of the majority at some point. A functioning democracy allows different individuals and groups to participate and have their turn in the majority.
Question 78: Why is it important for the majority to work with the minority in a democracy?
A. To ensure minority opinions are permanently suppressed
B. To represent the general will of all citizens
C. To eliminate social differences
D. To reduce transparency in governance
Answer: B. To represent the general will of all citizens. Democracy thrives when the majority collaborates with the minority to reflect diverse perspectives.
Question 79: What is one of the major threats to social harmony in a democracy?
A. Complete equality among all social groups
B. Rule by a single majority community based on race, religion, or language
C. Increased public debate
D. The participation of minorities in decision-making
Answer: B. Rule by a single majority community based on race, religion, or language. When one group dominates decision-making, it can threaten the social harmony and inclusiveness of a democracy.
Question 80: What can democracies do to prevent social divisions from becoming violent?
A. Suppress all minority opinions
B. Develop mechanisms for negotiation and compromise
C. Enforce uniform cultural practices
D. Exclude certain groups from public debate
Answer: B. Develop mechanisms for negotiation and compromise. Democracies often rely on negotiation and dialogue to resolve social conflicts and prevent violence.
Question 81: What is a defining feature of democracy in handling social conflicts?
A. Majority rule without input from minorities
B. Permanent exclusion of certain social groups
C. Respect for diversity and peaceful resolution of conflicts
D. Ignoring social divisions
Answer: C. Respect for diversity and peaceful resolution of conflicts. Democracies aim to manage social conflicts by respecting diversity and resolving issues through peaceful means.
Question 82: How can social divisions in democracies be managed without becoming explosive or violent?
A. By promoting authoritarian rule
B. By suppressing public debates
C. Through procedures that encourage competition and negotiation
D. By eliminating minority participation in governance
Answer: C. Through procedures that encourage competition and negotiation. Democracies use fair competition and negotiation to manage social divisions peacefully.
Question 83: What lesson can be drawn from the example of Sri Lanka in terms of social harmony?
A. Majority rule must always suppress minority views
B. Democracy fails to manage ethnic and social divisions
C. Democracy must prevent majority domination based on religion or ethnicity
D. Social harmony is best achieved through dictatorship
Answer: C. Democracy must prevent majority domination based on religion or ethnicity. Sri Lanka shows that democracies must be careful not to let one group dominate others.
Question 84: What does democracy require to truly accommodate social diversity?
A. Majority opinions should be permanent
B. All citizens should have an equal chance to be in the majority at different times
C. Minority groups should always dominate decision-making
D. The majority should never cooperate with the minority
Answer: B. All citizens should have an equal chance to be in the majority at different times. In a democracy, majority rule must be flexible, allowing different groups to have a turn in leadership.
Question 85: What ensures that democracy remains democratic in accommodating social diversity?
A. Exclusion of minorities
B. Allowing only the majority group to participate in governance
C. Ensuring that all citizens have an opportunity to be part of the majority
D. Suppressing social and ethnic differences
Answer: C. Ensuring that all citizens have an opportunity to be part of the majority. Democracy remains inclusive when everyone has the chance to participate and influence governance.
VII. Dignity and Freedom of the Citizens (MCQ 86 to 100)
Question 86: What is a key benefit of democracy in promoting dignity and freedom?
A. Complete control by the government
B. Equal rights and respect for all citizens
C. Elimination of public participation
D. Suppression of minority groups
Answer: B. Equal rights and respect for all citizens. Democracy ensures that every individual receives respect and has the freedom to participate in governance.
Question 87: How does democracy help in reducing conflicts related to individual dignity?
A. By eliminating freedom of speech
B. By promoting respect for all individuals
C. By allowing only the government to make decisionsv D. By suppressing public opinion
Answer: B. By promoting respect for all individuals. Democracy acknowledges the dignity of each individual, which helps reduce conflicts arising from disrespect.
Question 88: What is a unique feature of democracy compared to other forms of government?
A. It eliminates all forms of inequality
B. It promotes the dignity and freedom of every individual
C. It limits public participation
D. It allows rulers to ignore public opinion
Answer: B. It promotes the dignity and freedom of every individual. Democracy is built on the principle that all citizens deserve respect and freedom.
Question 89: How does democracy ensure the dignity of women and other disadvantaged groups?
A. By promoting their equal participation in decision-making
B. By restricting their access to political power
C. By ignoring their rights
D. By focusing solely on economic development
Answer: A. By promoting their equal participation in decision-making. Democracy encourages the inclusion and equal participation of all groups, including women and disadvantaged communities.
Question 90: In what way does democracy help to strengthen the claims of disadvantaged groups?
A. By suppressing their rights
B. By ignoring their demands
C. By legally recognizing their claims for equal status and opportunities
D. By eliminating public debates on equality
Answer: C. By legally recognizing their claims for equal status and opportunities. Democracy provides a framework for disadvantaged groups to claim equality and fight against discrimination.
Question 91: What is the relationship between democracy and freedom of speech?
A. Democracy suppresses freedom of speech
B. Democracy limits freedom of speech to certain groups
C. Democracy guarantees freedom of speech for all citizens
D. Democracy ignores the need for public expression
Answer: C. Democracy guarantees freedom of speech for all citizens. One of the key pillars of democracy is the protection of free speech and public debate.
Question 92: How does democracy empower individuals to fight against social injustices?
A. By restricting their rights
B. By giving them the legal means to challenge inequalities
C. By preventing them from participating in governance
D. By enforcing strict government control
Answer: B. By giving them the legal means to challenge inequalities. Democracy provides individuals with the tools and legal backing to address social injustices.
Question 93: What has been the impact of democracy on caste inequalities in India?
A. Caste-based inequalities have been completely eliminated
B. Democracy has strengthened the legal claims of disadvantaged castes
C. Democracy has ignored caste-based inequalities
D. Democracy has promoted discrimination based on caste
Answer: B. Democracy has strengthened the legal claims of disadvantaged castes. While caste inequalities persist, democracy has given these groups a platform to fight for equal rights.
Question 94: How does democracy handle conflicts related to individual freedom?
A. By eliminating individual freedoms
B. By enforcing strict control over personal lives
C. By creating legal frameworks that protect individual freedoms
D. By ignoring the rights of individuals
Answer: C. By creating legal frameworks that protect individual freedoms. Democracies ensure that individuals have the right to personal freedom and protection under the law.
Question 95: What is the role of democracy in transforming citizens’ attitudes toward power holders?
A. It makes citizens submissive to power holders
B. It allows citizens to criticize and hold power holders accountable
C. It eliminates the right to question authority
D. It prevents public scrutiny of leaders
Answer: B. It allows citizens to criticize and hold power holders accountable. Democracy empowers individuals to scrutinize and challenge those in power.
Question 96: How does democracy promote the dignity of women, despite historical male domination?
A. By enforcing traditional gender roles
B. By recognizing and protecting women’s rights legally and morally
C. By ignoring gender equality
D. By reducing women’s participation in politics
Answer: B. By recognizing and protecting women’s rights legally and morally. Democracy has provided a platform for women to challenge traditional inequalities and gain legal recognition of their rights.
Question 97: What does the continuous evolution of democracy demonstrate?
A. Democracy’s failure to meet people’s expectations
B. Democracy’s inability to address social issues
C. Democracy’s adaptability to new demands and expectations
D. Democracy’s fixed nature
Answer: C. Democracy’s adaptability to new demands and expectations. As democracy evolves, people expect more, and it continuously adapts to meet these new expectations.
Question 98: How do citizens express their dissatisfaction in a democracy?
A. Through violent revolts
B. By exercising their right to vote and engage in public debates
C. By ignoring elections
D. By refraining from participating in governance
Answer: B. By exercising their right to vote and engage in public debates. Democracy allows citizens to express their dissatisfaction through voting and public engagement.
Question 99: Why is the public expression of dissatisfaction considered a success of democracy?
A. It shows that people have no trust in the system
B. It demonstrates the failure of democratic governance
C. It reflects citizens’ awareness and ability to hold the government accountable
D. It prevents public debate on important issues
Answer: C. It reflects citizens’ awareness and ability to hold the government accountable. Public dissatisfaction indicates that people are actively engaged in democracy and expect better performance from their leaders.
Question 100: What makes democracy a preferred system for ensuring freedom and dignity?
A. Its ability to centralize power
B. Its respect for individual rights and freedoms
C. Its exclusion of minority voices
D. Its quick decision-making processes
Answer: B. Its respect for individual rights and freedoms. Democracy is preferred because it protects the dignity and freedom of its citizens.
Outcome of Democracy
Very Short Answer Questions
1. What is the basic outcome of democracy?
Answer: The most basic outcome of democracy is that it produces a government that is accountable to citizens and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens.
2. What are the common features of democracy in most of the countries of the world?
Answer: Most of the democratic countries of the world today have formal constitutions, they hold elections, they have parties and they guarantee rights of citizens.
3. Are non-democratic rulers quick and efficient in decision making? Explain.
Answer: It is true that non-democratic rulers do not have to bother about deliberations in assemblies or worry about majesties and public opinion. So, they can be very quick and efficient in decision making and implementation.
4. “In comparison to non-democratic government, decision of government takes time.” Does democracy pay its price? Explain.
Answer: The democratic governments take more time to follow procedures before arriving at a decision. But because it has followed procedures, its decisions may be both more to the people and more effective.
5. What do you understand by ‘transparency’ in democracy?
OR
Explain the meaning of transparency in democracy. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: In democracy, decision making are based on norms and procedures. A citizen has the right and the means to examine the process of decision making. This is known as transparency.
6. Are democracies corrupt? Explain your argument.
Answer: Democracies often frustrate the needs of the people and often ignore the demands of a majority of its population. The routine tales of corruption are enough to convince us that democracy is not free of this evil.
7. How far does economic inequalities exist in democratic countries?
Answer: In democracies, a small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. Not only that, their share in the total income of the country has been increasing. Those at the bottom of the society suffer.
8. How democracy is considered best to accommodate social diversity?
Answer: In democracy, we can certainly learn to respect social differences and we can evolve mechanism to negotiate the differences. In fact, democracy is best suited to reduce this outcome.
9. How does democracy remove the gap between majority and minority in the country?
Answer: Rule by majority means that in case of every decision or in case of every election, different persons and groups may and can form a majority. Democracy remains democracy only as long as every citizen has a chance of being in majority at some point of time.
10. Do you agree that democracy promotes dignity of the citizen? Explain.
Answer: Often conflicts arise among individuals because some feel that they are not treated with due respect. The passions for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy. Democracy no doubt promotes dignity of the citizen and treats everyone equally.
11. Has democracy in India straightened the claims of discriminated castes for equal status?
Answer: In India, these are instances still of caste-based inequalities and atrocities but these lack the moral and legal foundations. Democracy has helped providing equal status and equal opportunities to the discriminated castes in India.
12. Explain the dilemma with respect to the practical aspect of democracy.
Answer: As per principle, democracy seems good but fails to impress in practice. This dilemma provokes to give a thought to the outcomes of democracy. Do we prefer democracy over moral reasons? Or there are some sensible reasons to support democracy too?
13. Explain any one difference between a pressure group and a political party. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: One difference between a pressure group and a political party is Political parties contest elections and hold power in the government while pressure groups attempt to influence government policies.
14. Why is there an overwhelming support to democracy all over the world? Explain one reason. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: There is an overwhelming support to democracy all over the world: Because it is accountable, responsive and legitimate government.
Short Answer Type Questions
1. What is democracy? What are its various characteristics?
Answer: In modern usage, democracy is a system of government, in which the citizens exercise power. It is formed by two Greek words ‘demos’ and ‘Kratia’. ‘Demos’ means people and ‘Kratia’ means the government. Democracy, thus means ‘rule by the people.’ In a democratic set up, every citizen has a right to take a part in the decision making process. According to Abraham Lincoln, democracy is ‘government of the people, government by the people and the government for the people’ Citizens choose their representatives who would form the government.
Characteristics:
- It promotes equality among citizens.
- It looks after the interest of the people.
- It allows room to correct mistakes.
2. What are the prudential reasons to support democracy?
Answer: Over a hundred countries of the world today claim and practise some kinds of democratic politics. They have formal constitution, they hold elections, they have parties and they guarantee rights to citizens. While these features are common to most of them, these democracies are very much different from one another in terms of their social situations, their economic achievements and their cultures.
3. Should we blame democracy for socio-economic and political problems?
Answer: If some of our expectations are not met, we start blaming the idea of democracy. The first step towards thinking carefully about the outcomes of democracy is to recognise that democracy is just a form of government. It can only create conditions for achieving something. The citizens have to take advantage of those conditions and achieve their goals.
4. What are our expectations from democracy?
Answer: In a democracy, we are most concerned with ensuring that people have the right to choose their rulers and people have control over the rulers. Whenever possible and necessary, citizens should be able to participate in decision-making that affects them all. Thus, the most basic outcome of democracy should be that the government is accountable to the citizens and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens.
5. What is the normal procedure of a democratic government?
Answer: (i) It should hold regular, free and fair elections.
(ii) Open public debates on major policies and legislations.
(iii) Right to information about the government and its functioning should be provided to citizens.
6. On the basis of which values will it be a fair expectation that democracy should produce a harmonious social life? Explain. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: The values that are associated with democracy producing a harmonious social life are:
(i) Equality among all human beings.
(ii) Respect for individual freedom.
(iii) Democracies accommodate various social divisions.
(iv) Democracies reduce the possibility of tensions becoming explosive or violent.
(v) Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts.
7. How does democracy promote the dignity and freedom of an individual?
Answer: (i) Every individual wants respect from fellow beings.
(ii) Often conflicts arise among individuals because some feel that they are not treated with due respect.
(iii) The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy all over the world—in countries with democratic regimes as well as countries without democratic regimes.
For societies which have been built for long on the basis of subordination and domination, it is not a simple matter to recognise that all individuals are equal.
8. On what factors does the country’s economic development depend?
Answer: A country’s economic development depends on the following factors:
(i) Country’s population, size
(ii) Its global situation
(iii) Cooperation from other countries
(iv) Economic priorities adopted by the country
However, the difference in the rates of economic development between less developed countries with dictatorship and democracies is negligible.
9. Is it true that democracies are not very successful in reducing economic inequalities?
Answer: It is true. The following points justify that:
(i) A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a disproportionate share of wealth and income. Not only that, their share in the total income of the country has been increasing.
(ii) Those at the bottom of the society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining.
(iii) Sometimes, they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life, such as food, clothing, housing, education and health.
In actual life, democracies do not appear to be very successful in reducing economic inequalities.
10. How can you say that democracy is better than dictatorship?
OR
Which values make democracy better than any other form of government? Explain. [CBSE (F) 2017]
OR
Analyse any three values that make democracy better. [CBSE Delhi 2017]
Answer: (i) Democracy promotes equality among citizens as it is people’s own government.
(ii) It enhances the dignity of the individual
(iii) It also improves the quality of decision-making
(iv) It provides methods to resolve conflicts, if any
(v) Only democracy allows room to correct mistakes
(vi) It is a legitimate government
(vii) Gives equal status and respect to women and weaker sections.
(viii) It promotes transparency.
(ix) Values of social justice, equality, fraternity.
(x) It gives importance to public opinion.
(xi) It provides rights to people.
(xii) It gives the feeling of collective belonging.
(xiii) It encompasses the feeling of integrity secularism and tolerance.
(xiv) It inculcates the feeling of integrity feeling of integrity and dutifulness.
(xv) It may be slow, less efficient, not always very responsive or clean. A democratic government is the people’s own government.
(xvi) There is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world—in countries with democratic regimes as well as with non-democratic regimes.
11. How much time is taken in democracy to take decisions as compared to other governments?
Answer: (i) A government may take decisions very fast but it may take such decisions that are not accepted by the people and may, therefore, face problems.
(ii) In contrast, the democratic government will take more time to follow procedures before arriving at a decision.
(iii) But because it has followed procedures, its decisions may be both more acceptable to the people and more effective.
So, the cost of time that democracy pays is perhaps worth it.
12. How much transparency is there in democracy as compared to other governments?
Answer: (i) A citizen who wants to know if a decision was taken through the correct procedures can find that out. He/She has the right and the means to examine the process of decision-making. This is known as transparency.
(ii) This factor is often missing from a non-democratic government. Therefore, when we are trying to find out the outcomes of democracy, it is right to expect democracy to produce a government that follows procedures and is accountable to the people.
(iii) We can also expect that the democratic government develops mechanisms for citizens to hold the government accountable and mechanisms for citizens to take part in decision-making whenever they think fit.
13. “Democracy is accountable and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens.” Evaluate the statement. [CBSE (Comptt) 2017]
OR
“Democratic government is known as responsive government.” Assess the statement. [CBSE (Comptt) 2017]
Answer: Democracy is accountable and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens:
(i) The most basic outcome of democracy is that it produces a government that is accountable to the citizens, and responsive to the needs and expectations of the citizens. Economic growth and development –level of economic development is slow because of delay in decision making. Accommodation of social diversity – majority should work with minority. Dignity and freedom of citizens-every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings. Equality of women.
14. How does democracy stand better to any other form of government in promoting the dignity and freedom of the citizens? Explain with examples. [CBSE (Comptt) 2017]
Answer: Democracy stands better to any other form of government in promoting the dignity and freedom of citizens:
(i) The passion for respect and freedom are the basis of democracy which is recognized throughout the world in principle.
(ii) Dignity of women : Democracy provides dignity to women by giving them the freedom to fight for their rights.
(iii) Right to equality: equal status and equal opportunity has a legal sanction in democracy.
(iv) Individual freedom : In democracy every individual has the freedom to pursue his goal.
15. Explain briefly the outcome of democracy.
Answer: (i) The first step towards evaluating outcome of democracy is to recognise that democracy is just a form of government. It means democracy provides an opportunity and it is the citizens who can take advantage of it.
(ii) The most basic outcome of democracy is that it is accountable to citizens and responsive to their needs and expectations.
(iii) Another outcome of democracy is that it is a legitimate government. It means all decisions are taken as per the constitution only.
16. Why is there a sound support for the idea of democracy all over the world?
Answer: (i) It is so because a democratic government is people-run government duly elected by them.
(ii) It is a legitimate government since it follows all the laws provided in the constitution.
(iii) People wish to be ruled by the representatives elected by them. The voters enjoy to form political parties and elect the government of their choice.
17. “The economic growth rate in dictatorship is better than that in democratic rule.” Why is it so?
Answer: (i) The economic growth rate in all dictatorial regimes was 4.42 per cent as compared to all democratic regimes’ 3.95 per cent during the period 1995–2000.
(ii) In dictatorial regimes, the rules and regulations are rigid and compulsory. The citizens who disobey are severely punished.
(iii) In democratic regimes, as the leaders and bureaucrats think about their profits only, the government is not much keen to remove poverty and develop the country economically.
18. Suggest some broad guidelines that can be kept in mind while devising ways and means for political reforms in India. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Answer: Guidelines for political reform:
(i) Any legal change must carefully look at what results it will have on politics. Sometimes, the results may be counter-productive.
(ii) The main focus of political reforms should be on ways to strengthen democratic practice.
(iii) Any proposal for political reforms should think not only about what is a good solution but also about who will implement it and how?
19. “Democratic government is legitimate government”? Support the statement with arguments. [CBSE Delhi 2016]
OR
How is ‘democratic government’ a ‘legitimate government’? Explain with examples. [CBSE Delhi 2017]
Answer: Democratic government is a legitimate government: It may be slow, less efficient, not always very responsive or clean. But a democratic government is peoples’ own government. That is why there is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world. People wished to be ruled by representatives elected by them. They also believe that democracy is suitable for their country. Democracy’s ability to generate its own support is itself an outcome that cannot be ignored.
Democratic Government known as legitimate government:
(i) Democracy produce a government that follows and is accountable to the people.
(ii) It provides mechanism for citizens to hold the government accountable and allows citizens to take part in decision making whenever they think fit.
(iii) If you wanted to measure democracies on the basis of this expected outcome you would look for the following practices and institutions regular free and fair election, open public debate on major policies.
20. Democracy accommodates social diversities. Support the statement with examples. [CBSE (AI) 2016]
OR
How is social diversity accommodated in democracy? Explain with examples. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: “Democracy accommodates social diversities”.
Democracy develops a mechanism which successfully negotiates difference among ethnic population.
(i) Democracies develop a procedure to conduct their competition. This reduces the possibility of these tensions becoming explosive or violent.
(ii) No society can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different groups. But we can certainly learn to respect these differences and can evolve mechanism to negotiate these differences.
(iii) Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts is thus a definite plus point of democratic regimes.
(iv) For example: Belgium has successfully negotiated differences among ethnic population. This reduces the possibility of tensions.
21. “Democratic governments in practice are known as accountable.” Support the statement with arguments. [CBSE (F) 2016]
Answer: Democratic governments in practice are accountable:
(i) It is right to expect democracy to produce a government that follows procedures and is accountable to the people.
(ii) It is also expected that the democratic government develops mechanisms for citizens to take part in decision making whenever they think it is fit.
(iii) The democratic government is accountable to the people. If it ignores the will of the people, they will not elect their ruler in the next general election.
(iv) The procedures and decision making process should be transparent for democratic government to be accountable to the people.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Do democracies lead to peaceful and harmonious relations among citizens?
Answer: Democracies usually develop a procedure to conduct their competition. This reduces the possibility of these tensions becoming explosive or violent. No society can fully and permanently resolve conflicts among different groups. But we can certainly learn to respect these differences and we can also evolve mechanisms to negotiate the differences. Democracy is best suited to produce this outcome. Non-democratic regimes often turn a blind eye to or suppress internal social differences. Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts is, thus, a definite plus point of democratic regimes.
2. Is economic growth in democracies accompanied by increased inequalities among the people?
Answer: Democracies are based on political equality. All individuals have equal right in electing representatives. Parallel to the process of bringing individuals into the political arena on an equal footing, we find growing economic inequalities. A small number of ultra-rich enjoy a highly disproportionate share of wealth and incomes. Not only that, their share in the total income of the country has been increasing. Those at the bottom of the society have very little to depend upon. Their incomes have been declining. Sometimes, they find it difficult to meet their basic needs of life such as food, clothing, housing, education and health.
3. How far are democracies able to handle differences between various ethnic groups?
Answer: Democracies are able to accommodate various social divisions. These usually develop a procedure to reduce the possibility of tension between ethnic groups as they become explosive or violent sometimes. Democracy is best suited to reduce this outcome. Non-democratic regimes often turn a blind eye to or suppress social differences. Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts is, thus, a definite plus point of democratic regimes.
4. “What the most distinctive about democracy is that its examination never gets over.” Comment.
Answer: As democracy passes one test, it produces another test. As people get some benefits of democracy, they ask for more and want to make democracy even better. That is why, when we ask people about the way democracy functions, they always come up with more expectations and many complaints.
The fact that people are complaining is itself a testimony to the success of democracy. It shows that people have developed awareness and the ability to expect and to look at power holders critically and the high and the mighty. A public expression of dissatisfaction with democracy shows the success of the democratic project; it transforms people from the status of a subject into that of a citizen.
5. What outcomes are expected of a democracy?
Answer: (i) People should get a chance to choose their representatives without any fear.
(ii) Elections are held periodically on the basis of universal franchise.
(iii) Free and fair elections are conducted by an independent machinery.
(iv) The elected representatives are accountable to the people.
(v) There is more than one political party which competes for power.
(vi) Pressure and Interest groups play a prominent role in the system.
(vii) People are guaranteed fundamental rights like right to life, liberty, equality and religion by the constitution.
(viii) The constitution provides for an independent and impartial judiciary, which protects the rights of the people.
(ix) There should be a strong opposition which should act as a watchdog on government both inside and outside the Parliament.
(x) There should be an enlightened public opinion so that people can put pressure on government.
(xi) The constitution provides for a written set of roles, which divides power between the Centre and the state.
(xii) Freedom of the press should be allowed.
(xiii) Public order and decency should be maintained.
(xiv) The unity, integrity and sovereignty of the country should be maintained.
(xv) People should be vigilant and participate actively in the process of governance.
The first thing towards thinking carefully about the outcomes of democracy is to recognise that democracy is just a form of government. Democracy can only create conditions for achieving something.
6. Evidence shows that in practice, many democracies did not fulfil the expectation of producing economic development in the country. Validate the statement with the help of relevant example. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Answer: If we consider all democracies and all dictatorships for the fifty years between 1950 and 2000, dictatorships have slightly higher rate of economic growth. Economic development depends on several factors: country’s population size, global situation, cooperation from other countries, economic priorities adopted by the country, etc.
However, the difference in the rates of economic development between less developed countries with dictatorships and democracies is negligible. Overall, it cannot be said that democracy is a guarantee of economic development. But we can expect democracy not to lag behind dictatorships in this respect.
When such a significant difference in the rates of economic growth between countries under dictatorship and democracy, it is better to prefer democracy as it has several other positive outcomes.
7. How are the democratic governments better than the other forms of governments? Compare. [CBSE Delhi 2016]
OR
“Democracy is a better form of government than any other form of government.” Analyse the statement with arguments. [CBSE Delhi 2016]
Answer: The democratic governments are better than other forms of governments:
(i) Democratic governments have formal constitution, while not in other form of governments.
(ii) They hold regular elections, while not in other form of governments.
(iii) They have political parties, while not in other form of governments.
(iv) They guarantee rights of citizens, while not in the other form of governments.
(v) Such governments allow room to correct mistakes, while not in the other form of government.
(vi) Such government accommodates social diversities, while not in other form of government.
8. Describe any five characteristics of democracy. [CBSE (AI) 2017]
Answer: Democracy is a better form of government from any other form of government:
(i) Democracy promotes equality among citizens.
(ii) Enhances the dignity of the individual.
(iii) Improves the quality of decision making.
(iv) Provides method to resolve conflicts.
(v) Accountable, responsive and legitimate government.
(vi) Reduction of inequality and poverty.
(vii) It promotes transparency.
9. “Democracy stands much superior in promoting dignity and freedom of the citizens.” Justify the statement. [CBSE Delhi 2017, CBSE (AI) 2016]
Answer: “Democracy stands much superior in promoting dignity and freedom of the citizens”:
(i) Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings.
(ii) The passion for respect and freedom are basis of democracy.
(iii) Democracies throughout the world have recognized this. It has been achieved in various degrees in various democracies.
(iv) Long struggles by women have got them respect and equal treatment and now accepted as necessary ingredients of a democratic society
(v) In many democracies, women were deprived of their right to vote for a long time which they have achieved now.
(vi) In India, 1/3rd of seats have been reserved for women in local bodies.
(vii) Democracy has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and discriminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity.
(viii) Legal basis which works on the principle of individual freedom and dignity.
10. How does democracy produce an accountable, responsive and legitimate government? Discuss by giving five reasons. [CBSE Sample Paper 2016]
Answer: (i) In a democracy, people have the right to elect their rulers and participate in decision making that affects them all. Government thus, is accountable to the citizens and responsive to their needs and expectations.
(ii) Democracy is based on the idea of deliberation and negotiation, though it results in delays. It ensures that decision making is based on norms and procedures and allows transparency. Develops mechanisms for citizens to hold the government accountable.
(iii) Set up following practices and institutions: regular, free and fair elections; open public debate on major policies and legislations; and citizens’ right to information about the government and its functioning.
(iv) It may be reasonable to expect from democracy a government that is attentive to the needs and demands of the people and is largely free of corruption. Though the record of democracies is not impressive on these two counts.
(v) Democratic government is a legitimate government. It may be slow, less efficient, not always very responsive or clean, but is people’s own government. People wish to be ruled by representatives elected by them.
11. ‘‘A democracy must look after the interests of all, not just one section.’’ Support the statement with arguments. [CBSE (F) 2017]
Answer: Democracy must look after the interest of all because:
(i) Democracy believes in and work for equality.
(ii) It has the ability to handle social differences irrespective of religion or race or linguistic group, etc.
(iii) It gives equal treatment to women.
(iv) It cares equally for majority and minority.
(v) Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged.
(vi) It tries to provide equal opportunities to minority and depressed classes.
(vii) Ordinary citizens value their democratic rights.
(viii) Democracy shows that people have developed awareness.
(ix) It has the ability to expect and look critically at power holders.
12. ‘‘No party system is ideal for all countries and in all situations.’’ Analyse the statement. [CBSE (AI) 2017, CBSE (F) 2016]
Answer: Party system is not something any country can choose:
(i) It evolves over a long time, depending on the nature of society.
(ii) It depends on social and regional divisions.
(iii) It depends on history of politics and its system of elections.
(iv) These cannot be changed very quickly.
(v) Each country develops a party system that is conditioned by its special circumstances.
HOTS Questions (Higher Order Thinking Skills)
1. “There is an overwhelming support for the idea of democracy all over the world.” Support the statement.
Answer: Over a hundred countries of the world today claim and practise some kind of democratic politics. They have formal constitution, they hold elections, they have parties and they guarantee rights to citizens.
While these features are common to most of them, these democracies are very much different from one another in terms of their social situations, their economic achievements and their cultures. Democracy is a government that is attentive to the needs and demands of the people and largely free of corruption.
2. “Democratic government is attentive to the needs and demands of the people and is largely free of corruption.” Support your answer with arguments.
Or
Is democracy attentive to the needs of people? Is it free from corruption?
Answer: The record of democracies is not impressive on these two counts.
(i) Democracies often frustrates the needs of people and ignore the demands of a majority of its population.
(ii) The routine tales of corruption are enough to convince us that democracy is not free from this evil.
(iii) Democracies also give right to the citizens to choose their representatives. Whenever possible, people are able to participate in decision making. But their decisions are not often followed.
(iv) At the same time, there is nothing to show that non-democracies are less corrupt or more sensitive to the people.
3. How has corruption become a serious problem for Indian democracy?
Answer: Democracies often frustrate the needs of people and ignore demands of a majority of its population. It is an accepted fact that leaders use money to win votes and capitalists are supporting them. Nowadays we find that richer people are getting into politics, just to support parties and get their say in the parliament.
The native tales of corruption are enough to convince us that democracy is not free from this evil. Now many leaders are involved in scams which become a daily news in the newspaper. These leaders are mostly involved in corruption charges.
4. How are complaints treated as testimony to the success of democracy?
Answer: (i) Every individual wants to receive respect from fellow beings.
(ii) As people get some benefits of democracy, they ask for more and want to make democracy even better.
(iii) That is why, when we ask people about the way democracy functions, they will always come up with more expectations, and many complaints.
(iv) The fact that people are complaining is itself a testimony to the success of democracy.
(v) It shows that people have developed awareness and the ability to expect and to look critically at power holders and the high and the mighty.
(vi) A public expression of dissatisfaction with democracy shows the success of the democratic project. It transforms people from the status of a subject into that of citizens
JNV Chapter IV: VMC MCQs Chapter IV: Vidyalaya Management Committee (VMC) - MCQs Test your un...
