WELCOME TO PROMISEDPAGE
SMART LEARNING BLOG
HOME
Monday, August 4, 2025
Sunday, September 29, 2024
Money and Credit Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which one of the following is a formal source of credit?
(a) Traders
(b) Cooperative societies
(c) Moneylenders
(d) Friends and relatives
Answer
Answer: (b) Cooperative societies
Question 2.
Which one of the following is the appropriate meaning of collateral?
(a) It is the sum total of money borrowed from banks.
(b) The amount borrowed from friends.
(c) It is an asset of the borrower used as guarantee to a lender.
(d) The amount invested in a business.
Answer
Answer: (c) It is an asset of the borrower used as guarantee to a lender.
Question 3.
Which one of the following is a modern form of currency?
(a) Paper notes
(b) Gold
(c) Silver
(d) Copper
Answer
Answer: (a) Paper notes
Question 4.
Which one of the following is the newer way of providing loans to the rural
poor, particularly women?
(a) Cooperative Banks
(b) Grameen Banks
(c) Self-Help Groups
(d) Moneylenders
Answer
Answer: (c) Self-Help Groups
Question 5.
Which of the following is the main informal source of credit for rural
households in India?
(a) Friends
(b) Relatives
(c) Landlords
(d) Moneylenders
Answer
Answer: (d) Moneylenders
Question 6.
Name the system in which the double coincidence of wants is an essential
feature.
(a) Barter system
(b) Money economy
(c) Global economy
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Barter system
Question 7.
Grameen Bank of Bangladesh was started in
(a) 1960s
(b) 1970s
(c) 1980s
(d) 1990s
Answer
Answer: (b) 1970s
Question 8.
In a SHG, most of the decisions regarding loan activities are taken by
(a) Banks
(b) Members
(c) Non-government organisation
(d) Cooperative
Answer
Answer: (b) Members
Question 9.
Which of the following is not an informal source of credit?
(a) Money-lender
(b) Relatives and Friends
(c) Commercial Banks
(d) Traders
Answer
Answer: (c) Commercial Banks
Question 10.
In which country is the Grameen Bank meeting the credit needs of over 6
million poor people?
(a) Bhuta
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Bangladesh
(d) Nepal
Answer
Answer: (c) Bangladesh
Question 11.
Which is not the main source of credit from the following for rural households
in India?
(a) Traders
(b) Relatives and friends
(c) Commercial Banks
(d) Moneylanders
Answer
Answer: (a) Traders
Question 12.
What portion of deposits are kept by the banks for their day to day
transaction?
(a) 10%
(b) 15%
(c) 20%
(d) 25%
Answer
Answer: (b) 15%
Question 13.
Which households take more loans from the formal sector?
(a) Poor households and rich household.
(b) Well off households and households with few assets.
(c) Poor households and well off households
(d) Well off households and rich households.
Answer
Answer: (d) Well off households and rich households.
Question 14.
Which among these is an essential feature of barter system?
(a) Money can easily exchange any commodity
(b) It is based on double co-incidence of wants
(c) It is generally accepted as a medium of exchange of goods with money
(d) It acts as a measure and store of value
Answer
Answer: (b) It is based on double co-incidence of wants
Question 15.
Which one of the following is the main source of credit for the rich
households?
(a) Informal
(b) Formal
(c) Both formal and informal
(d) Neither Formal nor informal
Answer
Answer: (b) Formal
Question 16.
Which one of the following is not a formal source of credit?
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) State Bank of India
(c) Employers
(d) Co-operatives
Answer
Answer: (c) Employers
Question 17.
Which one of the following agencies issues currency notes on behalf of the
government of India?
(a) Ministry of Finance
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) State Bank of India
(d) World Bank
Answer
Answer: (b) Reserve Bank of India
Question 18.
Formal Sources of credit include :
(a) money lenders
(b) co-operatives
(c) Employers
(d) Finance companies
Answer
Answer: (b) co-operatives
Question 19.
Which one of the following is NOT an informal sector loans for poor rural
household in India?
(a) Commercial Banks
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Landlords
Answer
Answer: (a) Commercial Banks
Question 20.
Which one of the following is not a modern form of money?
(a) Demand Deposits
(b) Paper currency
(c) Coins
(d) Precious metals
Answer
Answer: (d) Precious metals
Question 21.
Identify the formal source of credit:
(a) Cooperative societies
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Traders
(d) Landlords
Answer
Answer: (a) Cooperative societies
Question 22.
Who helps the borrowers to overcome the problem of lack of collateral?
(a) Self-help group (SHG)
(b) State government
(c) Employers
(d) Moneylenders
Answer
Answer: (a) Self-help group (SHG)
Question 23.
Which of the following is not a modern form of money?
(a) Paper notes
(b) Demand deposits
(c) Silver coins
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Silver coins
Question 24.
Formal sources of credit include
(a) banks
(b) moneylenders
(c) employers
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (a) banks
Question 25.
Rate of interest charged by moneylenders as compared to that charged by banks
is:
(a) lower
(b) same
(c) slightly higher
(d) much higher
Answer
Answer: (d) much higher
Question 26.
Which state accounts for maximum percentage of SHGs (self-help groups) in bank
credit?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Kerala
(d) Karnataka
Answer
Answer: (a) Andhra Pradesh
Question 27.
Who supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector?
(a) Central Bank of India
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Moneylenders
(d) None
Answer
Answer: (d) None
Question 28.
At present which form of money is increasingly used apart from paper money?
(a) Commodity money
(b) Metallic money
(c) Plastic money
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Plastic money
Question 29.
Currency is issued in India by :
(a) commercial banks
(b) regional rural banks
(c) nationalised banks
(d) Reserve Bank of India
Answer
Answer: (d) Reserve Bank of India
Question 30.
The part of the total deposits which a bank keeps with itself in cash is
(a) zero
(b) a small proportion
(c) a big proportion
(d) 100 percent
Answer
Answer: (b) a small proportion
Question 31.
System of exchanging goods for goods is called:
(a) monetary system
(b) credit system
(c) barter system
(d) exchange system
Answer
Answer: (c) barter system
Question 32.
Money
(a) eliminates double-coincidence of wants
(b) acts as a common measure of value
(c) acts as a standard of deferred payments
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (d) all the above
Money and Credit Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which one of the following statements is most appropriate regarding a transaction made in money? [Delhi 2012]
(a) It is the easiest way
(b) It is the safest way
(c) It is the cheapest way
(d) It promotes trade
2. Which one of the following is the new way of providing loans to the rural poor? [Delhi 2012]
(a) Co-operative societies
(b) Traders
(c) Relatives and friends
(d) SHG’s
3. Which among the following authorities issues currency notes? [Delhi 2012]
(a) Government of India
(b) The State Bank of India
(c) Central Bank
(d) Reserve Bank of India
4. Banks provide a higher rate of interest on which one of the following accounts ? [AI 2012]
(a) Saving account
(b) Current account
(c) Fixed deposits for a long period
(d) Fixed deposits for a very short period
5. Which one of the following is the main source of credit for rich urban households in India ? [AI 2012]
(a) Formal sector
(b) Informal sector
(c) Moneylenders
(d) Traders
6. Which one of the following is an essential feature of the barter system?
(a) It promotes local market.
(b) It spreads social field of an individual.
(c) It requires double coincidence of wants.
(d) It is an easy way.
7. Which one of the following terms is not included against loans? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Interest rate
(b) Collateral
(c) Documentation
(d) Lender’s land
8. What is main source of income for banks? [CBSE CCE 2012]
(a) Interest on loans
(b) Interest on deposits
(c) Difference between the interest charged on borrowers and depositors
(d) None of these
9. In which one of the following systems exchange of goods is done without use of money? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Credit system
(b) Barter system
(c) Banking system
(d) Collateral system
10. Which of the following has an essential feature of double coincidence? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Money system
(b) Barter system
(c) Financial system
(d) Banking system
11. What percent of their deposits do bank hold as cash? [CBSE(CCE)2012]
(a) 50 percent
(b) 80 percent
(c) 15 percent
(d) 60 percent
12. Which of the following is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender? [CBSE(CCE)2012]
(a) Property
(b) Money
(c) Collateral
(d) Deposits
13. How many members a typical Self-Help Group Should have? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) 14 – 19
(b) 15 – 20
(c) 20 – 25
(d) 25 – 30
14. In a barter system: [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) Goods are exchanged for money.
(b) Goods are exchanged for foreign currency.
(c) Goods are exchanged without the use of money.
(d) Goods are exchanged on credit.
15. About what percentage of their deposits is kept as cash by the banks in India? [CBSE (CCE) 2012]
(a) 25 %
(b) 20 %
(c) 15 %
(d) 10 %
16. Why do banks keep a small proportion of the deposits as cash with themselves? [Delhi 2011]
(a) To extend loan to the poor.
(b) To extend loan facility.
(c) To pay salary to their staff.
(d) To pay the depositors who might come to withdraw money.
17. The currency notes on behalf of the Central Government are issued by whom? [Delhi 2011]
(a) State Bank of India
(b) Reserve Bank of India
(c) Punjab National Bank
(d) Central Bank of India
18. Which one of the following is not a feature of money? [AI 2011]
(a) Medium of exchange
(b) Lack of divisibility
(c) A store of value
(d) A unit of account
19. Professor Muhammad Yunus is the founder of which one of the following banks? [AI 2011]
(a) Cooperative Bank
(b) Commercial Bank
(c) Grameen Bank
(d) Land Development Bank
20. Which one of the following is a modern form of currency? [Foreign 2011]
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Copper
(d) Paper notes
21. The Informal source of credit does not include which one of the following? [Foreign 2011]
(a) Traders
(b) Friends
(c) Cooperative Societies
(d) Moneylenders
Additional Questions
22. Anything which is generally accepted by the people in exchange of goods and services
(a) Money
(b) Barter
(c) Credit
(d) Loans
23. Both parties agree to sell and buy each other’s commodities
(a) Measure of value
(b) Store of value
(c) Double coincidence of wants
(d) Credit
24. Money acts as an intermediate in the exchange process. Which function of money is highlighted here?
(a) Measure of value
(b) Medium of Exchange
(c) Store of value
(d) All of them
25. Modern forms of money include
(i) Gold
(ii) Paper Notes
(iii) Coins
(iv) Silver
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
26. Mpney is accepted as a medium of exchange because the currency is authorised by
(a) Private sector
(b) Public sector
(c) Government
(d) People
27. Deposits in the bank accounts can be withdrawn on demand, therefore these deposits are called
(a) Returnable deposits
(b) Acceptable Deposits
(c) Demand deposits
(d) None of the above
28. It is a paper instructing the bank to pay a specific amount from the person’s account to the person in whose name it has been made is
(a) Paper note
(b) Cheque
(c) Chit fund
(d) Credit card
29. Banks use the major portion of the deposits to
(a) Keep as a reserve so that people may withdraw
(b) Meet their routine expenses
(c) Extend loans
(d) Meet renovation of the bank
30. An agreement in which the lender supplies the borrower with money, goods or services in return for the promise of future payment.
(a) Credit (loan)
(b) Chit fund
(c) Bank
(d) Cheque
31. Salim, the shoe manufacturer, to meet expenses obtains loans from two sources.
(i) Asks leather supplier to supply leather on credit
(ii) Bank
(iii) Obtains loan in cash as advance payment
(iv) Relatives
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
32. Swapna is unable to repay the moneylender and she is caught in debt. She has to sell a part of the land to pay off the debt. This situation is an example of
(a) Debt-loss
(b) Debt-Insecurity
(c) Debt-trap
(d) All of them
33. Whether credit would be useful or not, depends on
(i) Whether there is some support in case of loss
(ii) Action of competitors
(iii) Market response
(iv) Risks in the situation
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
34. Terms of credit does not include
(a) Interest rate
(b) Collateral
(c) Cheque
(d) Mode of repayment
35. Krishak cooperative functioning in a village near Sonpur has ……………. farmers as members.
(a) 2500
(b) 2400
(c) 2350
(d) 2300
36. Formal sector loans include loans from
(i) Banks
(ii) Moneylenders
(iii) Cooperatives
(iv) Traders
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
37. Contribution of commercial banks as a source of credit for rural households in India in 2003 was
(a) 30 %
(b) 28 %
(c) 25 %
(d) 26 %
38. Organisation which supervises the credit activities of lenders in the informal sector.
(a) No organization
(b) Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
(c) State Government
(d) Central Government
39. Compared to the formal lenders, most of the informal lenders charge a much …………….. interest on loans
(a) Lower
(b) Constant
(c) Higher
(d) No interest
40. Formal sector meets only about …………… of the total credit needs of the rural people (in 2003)
(a) one third
(b) one fourth
(c) half
(d) whole
41. It is important that the formal credit is distributed more equally so that
(a) Poor can benefit from cheaper loans.
(b) Rich can get costly loans.
(c) Rich can get cheaper loans.
(d) None of the above.
42. After a year or two, if the SHG is regular in savings, it becomes eligible for availing loan from
(a) Cooperative societies
(b) Moneylenders
(c) Bank
(d) Traders
43. ……………. help borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral and also they are the building blocks of organization of the rural poor.
(a) Government
(b) Banks
(c) Private sector
(d) SHGs
44. Almost all of the borrowers of Grameen Bank of Bangladesh are
(a) Men
(b) Women
(c) Senior citizens
(d) All of them
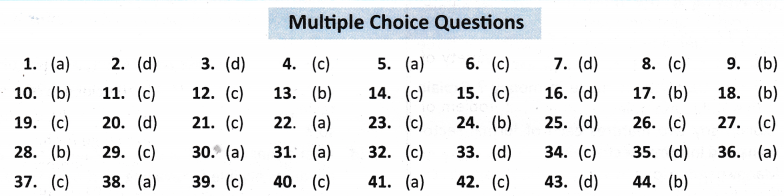
ANSWERS
JNV Chapter IV: VMC MCQs Chapter IV: Vidyalaya Management Committee (VMC) - MCQs Test your un...