Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
The Axis powers did not include
(a) Japan
(b) Italy
(c) Nazi Germany
(d) Britain
Answer
Answer: (d) Britain
Question 2.
The assembly line method is associated with the name of
(a) Henry Ford
(b) Rosa Parker
(c) Barry Parker
(d) E.T. Paull
Answer
Answer: (a) Henry Ford
Question 3.
The silk routes linked Asia with
(a) Europe
(b) Africa
(c) both (a) & (b)
(d) America
Answer
Answer: (c) both (a) & (b)
Question 4.
America was discovered by
(a) Marco Polo
(b) Christopher Columbus
(c) Henry Ford
(d) Cecil Rhodes
Answer
Answer: (b) Christopher Columbus
Question 5.
Tamil migrants went to
(a) Ceylon and Malaya
(b) Mauritius and Fiji
(c) Trinidad and Guyana
(d) Ceylon and Surinam
Answer
Answer: (a) Ceylon and Malaya
Question 6.
The group of powers collectively known as the Axis power during the Second
World War were:
(a) Germany, Italy, Japan
(b) Austria, Germany, Italy
(c) France, Japan, Italy
(d) Japan, Germany, Turkey
Answer
Answer: (a) Germany, Italy, Japan
Question 7.
Who among the following is a Nobel Prize winner?
(a) V.S. Naipaul
(b) J.M. Keynes
(c) Shivnarine Chanderpaul
(d) Ramnaresh Sarwan
Answer
Answer: (a) V.S. Naipaul
Question 8.
Which of the following statements correctly identifies the com laws?
(a) Restricted the import of corn to ; England
(b) Allowed the import of com to England
(c) Imposed tax on com
(d) Abolished the sale of com
Answer
Answer: (a) Restricted the import of corn to ; England
Question 9.
Who discovered the vast continent, later known as America?
(a) Vasco da Gama
(b) Christopher Columbus
(c) V.S. Naipaul
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Christopher Columbus
Question 10.
Why were the Europeans attracted to Africa?
(a) By its natural beauty
(b) By the opportunities for investment
(c) For its vast land resources and mineral wealth
(d) For recruitment of labour
Answer
Answer: (c) For its vast land resources and mineral wealth
Question 11.
Who discovered the vast continent, later known as America?
(a) Vasco da Gama
(b) Christopher Columbus
(c) V.S. Naipaul
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Christopher Columbus
Explanation:
Christopher Columbus accidentally discovered the vast continent later known
as America.
Question 12.
Name the writer who was a descendant of indentured labour migrants and also
got Nobel Prize?
(a) V.S. Naipaul
(b) Shivnarine Chanderpaul
(c) Ramnaresh Sarwan
(d) Ram Narain Tewary
Answer
Answer: (a) V.S. Naipaul
Explanation:
V. S. Nipal was one of the Nobel Prize winning writer who was a descendant
of indentured labour migrants.
Question 13.
What do you mean by Indentured labour?
(a) Unpaid labour
(b) A bonded labourer, to pay off his passage to a new country or home
(c) A slave brought in a share market
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) A bonded labourer, to pay off his passage to a new country or
home
Explanation:
A bonded labourer, under contract to work for a specific time for his
employer, to pay off his passage to a new country or home.
Question 14.
What were the product India carrying on an active coastal trade in ancient
times?
(a) Goods, money, skills and ideas abroad.
(b) Only goods
(c) Only Money
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Goods, money, skills and ideas abroad.
Explanation:
Indians carried goods, money, skills and ideas abroad, an active coastal
trade, as early as 3000 BC, linked Indus Valley Civilisation with
present-day West Asia.
Question 15.
What was the main reason behind the world shrank?
(a) European sailors found a sea route
(b) Production increase for European market
(c) Europe become the centre of the world trade
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) European sailors found a sea route
Explanation:
European sailors found a sea route to Asia, and also crossed the Atlantic
and discovered America, it become easier to reach any part of the world.
Question 16.
What do you mean by Group of 77 or G – 77?
(a) A protest against the western economic policies
(b) A group formed by western nations
(c) A group formed by the developing countries
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) A group formed by the developing countries
Explanation:
The Group of 77 (or G-77) is a group formed by the developing countries to
demand a new international economic order to demand a new international
economic order (NIEO).
Question 17.
What do you mean by international monetary system?
(a) It is the system of withdrawal of money.
(b) It is the system for deposit of money.
(c) It is the system linking national currencies and monetary system.
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) It is the system linking national currencies and monetary
system.
Explanation:
The international monetary system is the system linking national currencies
and monetary system. In this system, national currencies, for example the
Indian rupee, were pegged to the dollar at a fixed exchange rate.
Question 18.
What benefits did people get from trade in meat?
(a) Technology promoted better living conditions at home and support for
imperialism abroad
(b) Frozen meat transported to Europe reduced the cost of shipping meat and
made it affordable for the poor
(c) Reduce the risk of loss as the animal die during shipping.
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Explanation:
Till the 1870s, animals were shipped live and then slaughtered. But live
animals took up a lot of ship space. Many also died, fell ill, or lost
weight. Meat was hence an expensive luxury beyond the reach of the European
poor, refrigerated ships, enabled the transport of perishable foods over
long distances.
Question 19.
By which crucial influences Post-war reconstruction was shaped?
(a) The US emerged as the dominant country in the western world
(b) The collapse of capitalist world
(c) The emergence of Soviet Union as a world power
(d) Both a and c
Answer
Answer: (d) Both a and c
Explanation:
Post-war reconstruction was shaped by two crucial influences; the US emerged
as the dominant economic, political and military power in the western and
the Soviet Union emerged as a world power.
Question 20.
In between whom the Second World War was fought?
(a) America and Europe
(b) USA and Japan
(c) The Allies and the Axis powers
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) The Allies and the Axis powers
Explanation:
The Second World War was fought between the Allies (Britain, France, Soviet
Union and the US) and the Axis powers (Nazi Germany, Japan and Italy.
Question 21.
The concept of an assembly line to produce automobiles is adopted by whom?
(a) Henry Ford
(b) Ramesh Sarwan
(c) T.cuppola
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Henry Ford
Explanation:
Henry Ford adapted the assembly line of a Chicago slaughterhouse (in which
slaughtered animals were picked apart by butchers as they came down a
conveyor belt) to his new car plant in Detroit.
Question 22.
Which of these come under the Allies Power?
(a) Japan, Russia
(b) Britain, Germany
(c) Britain, France, Russia
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Britain, France, Russia
Explanation:
The Second World War was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi
Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (Britain, France, the Soviet Union
and the US
Question 23.
What do you mean by Rinderpest?
(a) A disease
(b) Name of a medicine
(c) A place
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) A disease
Explanation:
In Africa, in the 1890s, a fast-spreading disease of cattle plagues known as
rinderpest had a terrifying impact on people’s livelihoods and the local
economy.
Question 24.
What did the “Bretton Woods” associated with?
(a) A post-war international system to preserve economic stability
(b) A United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference
(c) A peace settlement
(d) Both a and b
Answer
Answer: (d) Both a and b
Explanation:
Bretton Woods” is associated with a post-war international system to
preserve economic stability and a United Nations Monetary and Financial
Conference held in July 1944, in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire.
Question 25.
What do you mean by tariff?
(a) Tax imposed on a country’s imports
(b) Tax imposed on a country’s exports
(c) Tax imposed on a country’s income
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) Tax imposed on a country’s imports
Explanation:
Tax imposed on a country’s imports from the rest of the world, levied at the
point of entry, for example border or airport.
Fill in the blanks:
1. From the 1900s India’s nationalist leaders began opposing the system of ……………… abusive.
Answer
Answer: indentured labour
2. The invention of ……………… enabled the transport of meat over long distances.
Answer
Answer: refrigerated ships
3. Africa had abundant land and a relatively small ………………
Answer
Answer: population
4. Rinderpest was a devastating ……………… disease.
Answer
Answer: cattle
5. Britain had a trade surplus with ………………
Answer
Answer: India
State whether the following statements are true or false:
1. V.S. Naipaul, the Nobel prize winning writer, is descended from indentured labour migrants from India.
Answer
Answer: True
2. Indian textiles faced stiff competition in international markets from the early nineteenth century.
Answer
Answer: True
3. America was the world’s leading economy before the First World War.
Answer
Answer: False
4. Agricultural regions and communities were the worst affected by the Great Depression.
Answer
Answer: True
5. Developing countries were greatly benefited by the Bretton Woods system.
Answer
Answer: False
Match the following:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) The First World War | a. 1939-1945 |
| (ii) The Second World War | b. late 1880s |
| (iii) The Great Depression | c. 1914-1918 |
| (iv) Rinderpest arrived in Africa | d. early 1920s |
| (v) The US economy boomed | e. 1929-1930s |
Answer
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) The First World War | c. 1914-1918 |
| (ii) The Second World War | a. 1939-1945 |
| (iii) The Great Depression | e. 1929-1930s |
| (iv) Rinderpest arrived in Africa | b. late 1880s |
| (v) The US economy boomed | d. early 1920s |
Social Science Quiz The Making of Global World Class 10
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Peoples livelihood and local economy of which one of the following was badly affected by the disease named Rinderpest [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Asia
(b) Europe
(c) Africa
(d) South America
2. Which of the following powerful weapons were used by the Spanish Conquerors to colonise America during mid 17th century. [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Coventional Military weapons
(b) Modern Military weapons
(c) Biological weapons
(d) Nuclear weapons
3. Why did the wheat price fall down by 50 per cent between 1928 and 1934? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Due to less production
(b) Due to floods
(c) Due to great depression
(d) Due to droughts
4. Most Indian indentured workers came from [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Eastern Uttar Pradesh
(b) North-eastern states
(c) Jammu and Kashmir
(d) None of these
5. Who adopted the concept of an assembly line to produce automobiles ?
(a) Henry Ford
(b) T. Cuppola
(c) V.S. Naipaul
(d) Samuel Morse
6. In ancient period the cowries were used as
(a) jewellery
(b) currency
(c) unit of Weight
(d) utensil
7. Which of the following diseases killed the majority of America’s original inhabitants ?
(a) Cholera
(b) Small Pox
(c) Typhoid
(d) Plague
8. In which place of India were the ‘canal colonies’ set up ?
(a) Punjab
(b) Haryana
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Assam
9. The fast spreading disease of cattle plague is known as
(a) cattle fever
(b) bubonic plague
(c) rinderpest
(d) chicken pox
10. Which of the following place was an important destination for indentured migrants ?
(a) Florida
(b) Melbourne
(c) Carribbean island
(d) Mexico
11. At which of the following states in USA was the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference held in 1944?
(a) New Hampshire
(b) New York
(c) San Francisco
(d) New Jersey
12. Which two institutions are well-known as Bretton Wood Institution ?
(a) UNICEF and IMF
(b) WHO and World Bank
(c) IMF and World Bank
(d) UNESCO and UNICEF
13. Who introduced the assembly line method for producing automobiles on a large scale ?
(a) V.S. Naipaul
(b) Henry Morton Stanley
(c) Henry Ford
(d) James Watt
14. Newly irrigated areas to settle peasants of Punjab were known as
(a) Watered colonies
(b) Canal colonies
(c) Punjab colonies
(d) Canalised colonies
15. The group of powers collectively known as the Axis power during the 2nd World War were
(a) Germany, Italy, Japan
(b) Austria, Germany, Italy
(c) France, Japan, Italy
(d) Japan, Germany, Turkey
16. Who among the following is a Nobel prize winner ?
(a) V.S. Naipaul
(b) J.M. Keynes
(c) Shivnarine Chanderpaul
(d) Ramnaresh Sarwan
17. Which of the following combination correctly indicates the three flows of international economic exchange ?
(a) Capital, goods, raw material
(b) Goods, metal, labour
(c) Goods, labour, capital
(d) Labour, capital, food grains
18. Which of the following statement correctly identifies the corn laws ?
(a) Restricted the import of corn to England.
(b) Allowed the import of corn to England.
(c) Imposed tax on corn.
(d) Abolished the sale of corn.
19. Which of the following refers to El Dorado ?
(a) A mythical animal
(b) A legendary god
(c) A fabled city of gold
(d) A sacred place of worship
20. Until 18th century which two countries were considered the richest in the world ?
(a) India and China
(b) China and Japan
(c) England and France
(d) England and Italy
21. Which of the following reflects the cultural fusion between India and Trinidad ?
(a) Native dancing
(b) Chutney music
(c) Religious practices
(d) Cottage industries
22.Transport of perishable goods over long distance was possible because of
(a) improved railways
(b) airline services
(c) refrigerated ships
(d) steamships
23. Which of the following sustained the African lives for centuries ?
(a) Industries and mines
(b) Mines and agriculture
(c) Land and livestock
(d) Production of consumer goods
24. In Trinidad what was referred as Hosay ?
(a) Annual Muharram procession marking a carnival
(b) Christmas Celebration
(c) Easter Festival
(d) New Year Celebration
25. What is meant by tariff ?
(a) Tax imposed on goods.
(b) Tax imposed on a country’s import from the rest of the world.
(c) Tax imposed on countries’ export to other countries.
(d) Tax imposed on handmade goods.
26. The World Bank was set-up to
(a) finance rehabilitation of refugees.
(b) finance post war construction.
(c) finance industrial development.
(d) help third world countries.
27. Mark the correct response out of the following :
(a) The silk route acted as a link between different countries.
(b) The silk route helped in cultural and commercial exchange.
(c) The silk route acted as a route for west bound silk cargos from China.
(d) All the above.
28. Why was the 19th century indenture described as a system of slavery ? Mark the most suitable statement.
(a) Lots of slaves worked in the plantation.
(b) The living and working condition of the indentured labourers were harsh.
(c) The indentured labourers did not have any rights and lived like slaves.
(d) The indentured labourers were not paid any salary.
29. Why did the export of fine Indian textile to England decline in 19th century ?
(a) Production of cotton declined
(b) Demand of Indian textile in England declined
(c) British government imposed heavy tariff on import of cotton textile
(d) Indian merchants refused to sell cotton to the British merchants
30. Which of the following resulted in Britain’s trade surplus ?
(a) British export to India was much higher than British imports from India.
(b) Britain’s export of opium from India increased.
(c) British import from India became higher than British export to India.
(d) Import of cotton from India was profitable for the British merchants.
31. Which of the following factor compelled the Africans to work for wages ?
(a) Poverty
(b) Loss of livestock
(c) Oppression by colonisers
(d) Willingness to work for wages
32. Which of the following is the most important cause for the Great Depression ?
(a) Decline in agricultural production
(b) Agricultural overproduction leading to fall of prices in agricultural goods
(c) Loss of employment leading to poverty
(d) Closure of banks and factories
33. Why were the Europeans attracted most to Africa ?
(a) By its natural beauty
(b) By the opportunities for investment
(c) For its vast land resources and mineral wealth
(d) For recruitment of labour
34. Which of the following enabled the Europeans to conquer and control the Africans ?
(a) Victory in war
(b) Control over the scarce resource of cattle
(c) Death of Africans due to rinderpest
(d) Lack of weapons in Africa to fight against the Europeans
35. Which of the following is the direct effect of Great Depression on Indian Trade ?
(a) Peasants and farmers suffered
(b) Indian exports and imports nearly halved between 1928-1934
(c) Peasants’ indebtedness increased
(d) Led to widespread unrest in rural India
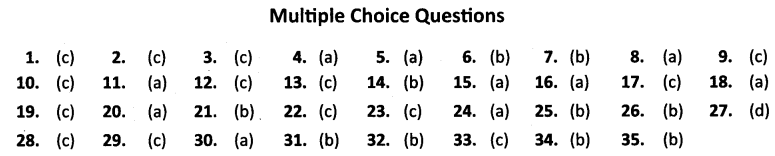
ANSWERS
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 History Chapter 3 The Making of A Global World
1. Give two examples of different types of global exchanges which took place before the seventeenth century, choosing one example from Asia and one from the Americas.
Ans: The examples of the different types of global exchanges that took place before the seventeenth century are as follows:
Europe and Asian countries exchanged Spices and Textiles for Gold.
America exchanged food and Gold with the European nations during the Colonial period.
2. Explain how the global transfer of disease in the pre-modern world helped in the colonisation of the Americas.
Ans: The Europeans were immune to the diseases but the natives of other nations outside of Europe were not. So, when they were infected with the diseases, their population suffered as they had to fight from within and this made them weaker and also drained their resources. So, Europeans were able to colonise them easily.
3. Write a note to explain the effects of the following:
(a) The British government’s decision to abolish the Corn Laws.
Ans: Due to the abolition of corn laws, the British farmers migrated to cities and took up other professions and eventually led to high industrial growth.
(b) The coming of rinderpest to Africa.
Ans: Due to rinderpest, the livelihoods of the Africans were destroyed and this made the Europeans to colonise the Africans easily.
(c) The death of the working-age in Europe because of the World War.
Ans: Due to the death of young men in World Wars, the women came out to work and they improved their position in the society.
(d) The Great Depression on the Indian economy.
Ans: The great depression led to loss in revenue for the farmers of India s the export prices fell drastically. However, the British Government did not decrease the taxes and this led to a massive unrest in India which paved the way for Indian Independence a few years later.
(e) The decision of MNCs to relocate production to Asian countries.
Ans: Due to the relocation of production to Asian countries, the Asian economies grew manifold and there was an increase in employment. The profits of the MNCs increased and the West also prospered due to which Global Production Networks were formed.
4. Give two examples from history to show the impact of technology on food availability.
Ans: Here are the two examples from history to show the impact of technology on food availability:
Faster railways, lighter wagons and larger ships led to the transport of food quickly from which decreased the cost of food.
Refrigerated ships facilitated the transport of perishable goods to far off nations.
5. What is meant by the Bretton Woods Agreement?
Ans: The Bretton Woods Agreement was signed in July 1944 at Bretton Woods in New Hampshire, USA by which the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank were established to preserve global economic stability and employment in the industrialised nations.
6. Imagine that you are an indentured Indian labourer in the Caribbean. Drawing from the details in this chapter, write a letter to your family describing your life and feelings.
Ans: Here is a sample letter:
Dear Family Members,
I hope you all are doing great and are fine there. This letter is all about my life here in the Caribbean where I am an indentured labour.
When I came here, life seemed to be very hard and it came as a surprise upon arrival. However, I am hopeful to come out of it very soon. Although life here is full of struggles and hardships, I did not choose all of this willingly. The contract was made lucrative only on the basis of false information and promises. I am a slave here and do not make a lot of money. However, I believe that this shall pass soon.
Your Son,
Manish
7. Explain the three types of movements or flows within international economic exchange. Find one example of each type of flow which involved India and Indians, and write a short account of it.
Ans: The three types of movements or flows within the international economic exchange are:
Trade Flow
Human Capital Flows
Capital Flows
Food such as potatoes, soya, groundnuts, chillies, etc. came to India from America.
Indentured labour was provided for mines, plantations and factories abroad which led to colonial domination of the British.
United Kingdom took many loans from USA to finance the World War. As India was an English colony, the impact of these loans was seen in India and it affected the Indian economy and people.
8. Explain the causes of the Great Depression.
Ans: The Great Depression was a caused due to the following factors:
Income and Prosperity in USA increased as it was very less affected by World War I. This caused an increase in demands and due to less production, inflation increased.
The stock exchanges crashed in 1929 which created panic among investors and depositors as they lost money and started accumulation of wealth.
Banks were closed and companies failed to get capital for investments.
9. Explain what is referred to as the G-77 countries. In what ways can G-77 be seen as a reaction to the activities of the Bretton Woods twins?
Ans: G-77 countries is an abbreviation for a group of 77 countries that had demanded a new international economic order which would give them more control over their natural resources. The G-77 was a reaction to the activities of the Bretton Woods twins as the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank were designed to meet the financial needs of only industrialised and developed countries.
The Making of Global World SAQ CBSE Class 10 Social Sciences
Q.1. ‘The pre-modern world shrank greatly in the 16th century.’ Explain.
Ans. (i) Because the European sailors found a sea route to Asia and successfully crossed the western ocean to America. The Portuguese and the Spanish conquests and colonialisation of America was decisively under way by the mid-16th century.
Precious metals, particularly silver, from mines located in presently Peru and Mexico enhanced Europe’s wealth and financed its trade with Asia.
Q.2. What were Corn Laws ? Why were these Laws abolished ? [CBSE 2009 (F) Sept. 2010, 2014]
Ans. The Corn Laws were British trade laws to regulate the export or import of corn.
(i) These laws were abolished :
(ii) Because restriction of imports lead to high food prices.
(iii) These laws restricted the free trade. Landlords, industrialists and urban dwellers were against these laws.
Q.3. Highlight three main features of life of African people before the coming of Europeans. [CBSE 2013]
Ans. (i) Africa had abundant land and a relatively small population.
(ii) For centuries, land and livestock sustained African livelihoods. Agriculture and animal rearing was the main occupation of the people. Most of the villages and families were self-sufficient.
(iii) People rarely worked for a wage. There were few consumer goods that wages could buy.
Q.4. What were the main reasons for the attraction of Europeans to Africa ? [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2014]
Ans. (i) Europeans were attracted to Africa in search of valuable minerals like gold, coal, silver, etc.
(ii) They were attracted to Africa due to its vast resources of land.
(iii) They went to Africa hoping to establish plantations and mines.
Q.5. Give three examples to show that the world changed with the discovery of new sea routes to America. [CBSE Sept. 2010, 2011, 2012]
Ans. (i) Before the discovery of the sea routes, America had been cut off from regular contact with the rest of the world for millions of years. But from the sixteenth century, its vast lands and abundant crops and minerals began to transform trade and lives everywhere.
(ii) Precious metals, particularly silver, from mires located in present day Peru and Mexico also enhanced Europe’s wealth and financed its trade with Asia. Legends spread in seventeenth-century Europe about South America’s fabled wealth. Many expeditions set off in search of El Dorado, the fabled city of gold
(iii) With the discovery of sea routes three types of movements or flows became prominent. i.c\. the flow of goods, labour and capital.
Q.6. “India played a crucial role in the late 19th century world economy”. Explain. [CBSE 2014]
Ans. (i) Britain had a ‘trade surplus’ with India. Britain used this surplus to balance its trade deficits with other countries.
(ii) Britain’s trade surplus in India also helped pay the so-called ‘home charges’ that included private remittances home by 3ntish officials and traders, interest payments or. India’s external debt, and pensions of British officials in India.v (iii) in the nineteenth century, hundreds of thousands of Indian and Chinese labourers went to work on plantations in mines anc in rood and railway construction projects around the world.
(iv) India also provided raw material to the developing industries of the world.
(v) India become a major market for the final goods: especially cotton textile.v Q.7. Name any two world institutions which were established under the Bretton Woods. Also mention one objective of each.v Ans. (i) International Monetary Fund.
(ii) World Bank.
Objective :
(a) IMF To deal with external surpluses and deficits o! its member nations.
(b) IBRD – To finance post-war reconstruction.
Q.8. Why thousands of people fled Europe for America in the 19th century ?
Or
Why did thousands of people flee away from Europe to America in the 19th century ? Give any three reasons. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Ans. (i) Until the 19th century, poverty and hunger were common in Europe.
(ii) Cities were crowded and deadly diseases were widespread.
(iii) Religious conflicts were common and religious dissenters were persecuted So people migrated from Europe to America.
Q.9. “Economists of the 19th century identify three types of movements or ‘flows’ within international economic exchanges.” Explain. [CBSE Sept. 2011. 2012]
Ans. (i) The flow of trade : The flow of trade refers largely to trade in goods. For example, wheat travelled from Russia, America and Australia to Britain.
(ii) The flow of labour : This includes the migration of people in search of employment. For example, more than 50 million people migrated from Europe to America and Australia In search of jobs.
(iii) The movement of capital : This covers the movement of capital for short-term or long-term investments over long distances. For example, capital flowed from financial centres such as London to other parts of the world.
Q.10. Explain indentured labour with lire help of an example.
Ans. A bonded labourer under contract to work for an employer tor a specific period of rime, to pay off a passage a new country or home. In the nineteenth century, hundreds of thousands of Indian and Chinese labourers went to work on plantations, in mines and ill roads and railway construction projects around the world.
In India, indentured labourers were hired under contracts which promised the return travel to India after they had worked five years on their employer’s plantation.
Q.11. Why did the European employers find it difficult to recruit labour in Africa ? Give two methods they used to recruit and retain labour. [CBSE 2011)
Or
Why was there a shortage of labour willing to work for wages in Africa in the 1890s ? How did Europeans try to recruit and retain labour ? Explain any two methods. [CBSE 2012]
Or
What methods were used by the European employers to recruit and retain the African labourers ?
Ans. The European employers found it difficult to recruit labour in Africa because historically. Africa had abundant land and a relatively small population. For centuries, land and livestock sustained African livelihood and people rarely worked for wages.
Methods to recruit and retain labour :
(i) Heavy taxes : Tile colonial government started imposing heavy taxes which could be paid only by working for wages on plantations and mines.
(ii) New inheritance laws : Inheritance laws were changed so that the peasants were displaced from land: only one member of a family was allowed to inherit land, others were pushed into the labour market
(iii) Restriction on movement : Miners were also enclosed in compounds, and were not allowed to move about freely.
Q.12. Mention any four factors responsible for indentured labour.
Ans. (i) Decline of cottage industry in India.
(ii) Increase in land rents.
(iii) Loss of cattle wealth due to rinderpest in Africa.
(iv) Unemployment and poverty.
Q.i3. What was the impact of industrialisation in Britain on Indian economy ?
Ans. (i) With industrialisation, the British cotton manufacturers began to expand and industrialists pressurised the government to restrict the cotton imports, and protect the local industries. Tariffs were imposed on doth imports into Britain. Consequently, the inflow of fine Indian cotton began to decline.
(ii) From the early nineteenth century. British manufacturers also began to search the overseas markets for their cloth.
(iii) The British machine-made textile products started giving a tough competition to the Indian textile industry at home.
So there was a decline in the share of cotton textiles from some 30 per cent around 1800 to 15 per cent by 1815. By the 1870s, this proportion had dropped to below 3 percent.
Q.14. “India played a crucial role in the late 19th century world economy.” Explain by giving an example.
Or
What was the importance of the Indian trade for the Britishers ?
Or
How did India play a crucial role in the nineteenth century world economy ? Explain with examples. [CBSE Comp. (O) 2008]
Ans. (i) Trade Surplus : Britain had a trade surplus with India, i e., a situation under which the value of exports is more than the imports. Britain used this surplus to balance its trade deficit with other countries.
(ii) Home charges : Britain’s trade surplus in India also helped to pay the so called ‘home charges’ that included private remittances home by British officials and traders, interest payments on India’s external debts and pensions of the British officials in India.
(iii) Major supplier of cotton : India remained a major supplier of raw cotton to Britain which was required to feed the cotton textile industry of Britain.
(iv) Supplier of indentured workers: Many indentured workers from Bihar. Uttar Pradesh, Central India migrated to other countries to work in mines and plantations.
Q.15. Name the countries involved in the First World War.
Ans. The war was the outcome ol the rivalry between the two strong armed camps or the European powers, i.e.. Triple Alliance and Triple Entente or the Central Powers.
On the one side were the Allies – Britain. France and Russia (later joined by the US) and on the opposite side were the Centre Powers – Germany, Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Turkey.
Q.16. What is NIEO ?
Or
Why did Group 77 countries demand a New International Economic Order ? Explain. [CBSE 2009 (D). Sept, 2010]
Or
Why did most of the developing countries organise themselves as a group — the Group of 77 (G-77) ? [CBSE 2012)
Ans. NIEO is the New International Economic Order. NIEO was a set of proposals put forward during the 1970s by the developing countries with the following main objectives:
(i) To revise the international economic system in favour of the developing countries.Financial news subscriptions
(if) The developing nations wanted a system that would give them a real control over their natural resources.
(iii) The developing countries wanted to set up a system under which they could get a fairer price for raw materials, and better access for their manufactured goods in the developed countries markets.
(iv) Developing countries must be entitled to regulate and control the activities of the Multinational Corporations (MNCs) .
Q.17. Mention the impact of the First World War on agricultural economies.
Ans. (i) The agricultural economies also suffered because of First World War.
(ill Before the War. Eastern Europe was a major supplier of wheat in the world market.
{iii) When this supply was disrupted during the First World War. wheat production of Canada. America and Australia expanded dramatically. But once the War was over, production in Eastern Europe revived and created a glut in the wheat output. Grain prices fell, rural income declined and farmers fell deeper into debt.
Q.18. ‘The First World War was modern industrial war’. Explain.
Or
Explain how the First World War was so horrible a war like none other before. [CBSE 2010 (0)]
Or
How far is it correct to say that “The First World Wax was the First modem industrial war”? Explain. [CBSE Sept. 2010]
Ans. i) The First World War saw the use of machine guns, tanks, aircraft, chemical weapons, etc. on a massive scale.V (ii) These were all increasingly products of modern large-scale industry. To fight the war. millions of soldiers had to be recruited from around the world. and moved to the front lines on large ships and trains.
(iii) The scale of death and destruction – 9 million dead and 20 million injured – was unthinkable before the industrial age, without the use of industrial arms.
Q.19. What is the difference between fixed exchange rate and floating exchange rate ?
Ans. Difference table (Image)
Q.20. “The First World War was fought between two power blocs” Explain.
Ans. The First World War was fought from 1914 – 1918. On the one side were the Allies – Britain. France and Russia (later joined by the US): and on the opposite side were the Central Powers – Germany. Austria – Hungary and Ottoman Turkey.
Q.21. What was mass production? Explain its impact on the world economy of earlier 20th century.
Ans. Production of goods on large-scale with the help of machines is known as mass production.
Impact :
(i) Mass production lowered costs and prices of engineered goods Thanks to higher wages, more workers could now afford to purchase durable consumer goods such as cars. Car production in US rose from 2 million in 1919 to more than 5 million in 1929.
(ii) The demand for refrigerators, washing machines, etc. was also fuelled by a boom in house construction and home ownership, financed once again by loans.
(iii) The housing and consumer boom of the 1920s created the basis of prosperity in the US. Large investments in housing and household goods seemed to create a cycle of higher employment and incomes, rising consumption demand, more investment, and yet more employment and incomes.
Q.22. Write any three factors responsible for indentured labour migration from India. [CBSE Sept. 2010. 2013]
Ans. (i) Most Indian indentured workers came from the present day regions of eastern Uttar Pradesh. Bihar. Central India and the dry- districts of Tamil Nadu. In the mid-nineteenth century these regions experienced many changes – cottage industries declined, land rents rose, lands were cleared for mines and plantations. All this affected the lives of the poor, they failed to pay then rents, became deeply indebted.
(ii) On the other hand workers were required in other countries for plantations, mines, road and railway construction projects.
(iii) In hope for better future in other countries many workers from India started migrated in other countries.