WELCOME TO PROMISEDPAGE
SMART LEARNING BLOG
HOME
Sunday, August 3, 2025
Sunday, September 29, 2024
Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 MCQs Questions with Answers
Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not considered a sacred tree in India
(a) Peepal
(b) Neem
(c) Banyan
(d) Mango
Answer
Answer: (b) Neem
Question 2.
The Buxa Tiger Reserve in West Bengal has been threatened about the loss of
habitat of many species due to
(a) Industrial development
(b) Agricultural expansion
(c) Port activities
(d) Mining
Answer
Answer: (d) Mining
Question 3.
What was the aim of Chipko movement?
(a) Human rights
(b) Political rights
(c) Agricultural expansion
(d) Forest conservation
Answer
Answer: (d) Forest conservation
Question 4.
The Mundas and Santhals of Chhota Nagpur region worship which one of the
following trees?
(a) Mahua
(b) Mango
(c) Peepal
(d) Tamarind
Answer
Answer: (a) Mahua
Question 5.
The species which are in danger of extinction are called:
(a) Vulnerable species
(b) Rare species
(c) Endangered species
(d) Normal species
Answer
Answer: (c) Endangered species
Question 6.
The Himalayan brown bear is an example of:
(a) Vulnerable species
(b) Rare species
(c) Endemic species
(d) Extinct species
Answer
Answer: (b) Rare species
Question 7.
The Asian cheetah was declared extinct in India in the year:
(a) 1951
(b) 1952
(c) 2010
(d) 1975
Answer
Answer: (b) 1952
Question 8.
The Himalayan yew is:
(a) an insect
(b) a medicinal plant
(c) a mammal
(d) a bird
Answer
Answer: (b) a medicinal plant
Question 9.
Teak monoculture has damaged the natural forests in:
(a) Ganga Plain
(b) South India
(c) Brahmaputra Plain
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) South India
Question 10.
How many tiger reserves are there in India:
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 27
(d) 29
Answer
Answer: (c) 27
Question 11.
Which one of the following is not considered a sacred tree in India?
(a) Peepal
(b) Neem
(c) Banyan
(d) Mango
Answer
Answer: (b) Neem
Question 12.
India has nearly …………… percent of total number of species in the world
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 8
(d) 2
Answer
Answer: (c) 8
Question 13.
When was Asiatic Cheetah declared extinct in India?
(a) in 1958
(b) in 1989
(c) in 1922
(d) in 1952
Answer
Answer: (d) in 1952
Question 14.
The Buxa Tiger Reserve is situated in which of the following states?
(a) Madhya Pradesh
(b) West Bengal
(c) Gujarat
(d) Orissa
Answer
Answer: (b) West Bengal
Question 15.
How many species of flora are found in India?
(a) 81000
(b) 47000
(c) 15000
(d) 41000
Answer
Answer: (b) 47000
Question 16.
Sariska wildlife sanctuary is located in which state?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Gujarat
(d) West Bengal
Answer
Answer: (a) Rajasthan
Question 17.
Which one of the following belongs to vulnerable species?
(a) Black buck
(b) Crocodile
(c) Indian rhino
(d) Blue sheep
Answer
Answer: (d) Blue sheep
Question 18.
Which of the following types of species are known as the extinct species?
(a) Species whose population levels are normal
(b) Whose population has declined
(c) Species with small population
(d) Species which are not found
Answer
Answer: (d) Species which are not found
Question 19.
Which one of the following states has the largest area under permanent
forests?
(a) Bihar
(b) Kerala
(c) Madhya Pradesh
(d) Uttar Pradesh
Answer
Answer: (c) Madhya Pradesh
Question 20.
Which of the following is an extinct species?
(a) Blue sheep
(b) Asiatic cheetah
(c) Black buck
(d) Asiatic elephant
Answer
Answer: (b) Asiatic cheetah
Question 21.
Forests and wastelands belonging to both private individuals and government
are known as:
(a) Sacred groves
(b) Reserved forest
(c) Protected forests
(d) Unclassed forests
Answer
Answer: (d) Unclassed forests
Question 22.
Which of the following species was included for the first time in list of
protected species in 1991?
(a) Insects
(b) Fishes
(c) Plants
(d) Reptiles
Answer
Answer: (c) Plants
Question 23.
In which of the following states, a very high percentage of its forests is
managed by local communities?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Andhra Pradesh
(d) Himachal Pradesh
Answer
Answer: (b) Arunachal Pradesh
Question 24.
What is the Himalayan Yew?
(a) A type of deer
(b) A medicinal plant
(c) A species of bird
(d) A food crop grown in the Himalayas
Answer
Answer: (b) A medicinal plant
Question 25.
Cleaning of forests is still continuing in Madhya Pradesh mainly due to which
of the following reasons?
(a) Dolomite mining
(b) Commercial plantations
(c) Industrialisaiton and urbanisation
(d) Narmada Sagar (River Valley) Project
Answer
Answer: (d) Narmada Sagar (River Valley) Project
Forest and Wildlife Resources Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Multiple Choice Questions
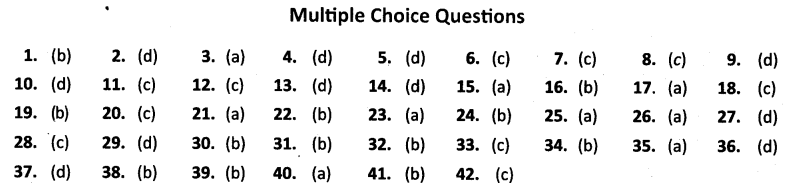
Previous Years’ Questions
1. Which one of the following .s not considered a sacred tree in India [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Peepal
(b) Neem
(c) Banyan
(d) Mango
2. What was the aim of Chipko movement ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Human rights
(b) Political rights
(c) Agricultural expansion
(d) Forest conservation
3. Which one of the following is an example of endemic species ? [CBSE (CCE) 2011]
(a) Nicobar Pigeon
(b) Asiatic Buffalo
(c) Horn Bill
(d) Black buck
NCERT Questions
4. Which of these statements is not a valid reason for depletion of flora and fauna ?
(a) Agricultural expansion.
(b) Large scale developmental projects.
(c) Grazing and fuelwood collection.
(d) Rapid industrialisation and urbanisation.
5. Which of the following conservation strategies do not directly involve community participation.
(a) Joint Forest Management
(b) Beej Bachao Andolan
(c) Chipko Movement
(d) Demarcation of Wildlife Sanctuaries
Additional Questions
6. The total forest cover in the country is about …………….
(a) 18.1%
(b) 22.1%
(c) 19.3%
(d) 11.5%
7. Most of the forests in the North eastern states belong to the category of …………..
(a) Wastelands
(b) Protected forests
(c) Unclassed forests
(d) Mangroves
8. Endemic species refers to
(a) Species which are extinct.
(b) Species which are declining.
(c) Species which are confined to specific areas only.
(d) Species which are normal.
9. Periyar Tiger reserve is located in
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Tamil Nadu
(d) Kerala
10. ‘Chipko movement’ is a programme started towards conservation of …………….
(a) Soil
(b) Water
(c) Minerals
(d) Forests
11. IUCN refers to
(a) International Understanding and Convention of Nature
(b) International Unity and Conservation of Nature
(c) International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources
(d) Indian Union for Conservation of Natural Beauty
12. Forests play a key role in the ecological system because
(a) it supports a large number of animals
(b) they are important for tourism.
(c) they are the primary producers on which all other living things depend.
(d) they provide us with many useful things.
13. The area of forest converted into agricultural land between 1951 to 1980 is about
(a) 25,000 sq. km.
(b) 20,000 sq. km.
(c) 23,000 sq. km.
(d) 26,200 sq. km.
14. The Buxa Tiger Reserve in West Bengal has been threatened about the loss of habitat of many species due to
(a) Industrial development
(b) Agricultural expansion
(c) Port activities
(d) Mining
15. Which group of people in India are responsible for maximum ecological destruction ?
(a) richest 5 percent
(b) poorest 25 percent
(c) tribal communities
(d) slum dwellers
16. Indian Wildlife Protection Act was implemented mainly to
(a) protect certain animals.
(b) protect the remaining population of certain endangered species.
(c) protect the tigers.
(d) protect aquatic animals.
17. The hunting and trade of which animals have been given full or partial legal protection in India ?
(a) Indian lion
(b) Indian elephant
(c) Black buck (Chinkara)
(d) Great Indian bustard (Godawan)
18. In India, forest and wildlife resources are owned and managed by
(a) Private individuals
(b) Communities
(c) The Government
(d) Others
19. Reserved forests refers to
(a) Forests protected from further depletion
(b) Forests meant for their valuable timber and other forest produce
(c) Conservation of some species
(d) Conservation of animals
20. The forests belonging to both government and private individuals and communities are called …………..
(a) Protected Forests
(b) Open Forests
(c) Unclassed Forests
(d) Reserved Forests
21. The Mundas and Santhals of Chhota Nagpur region worship which one of the following trees ?
(a) Mahua
(b) Mango
(c) Peepal
(d) Tamarind
22. Which one of the following is a farmers movement initiated in Tehri ?
(a) Tehri Andolan
(b) Beej Bachao Andolan
(c) Appease Movement
(d) Green Revolution
23. The main objective of Joint Forest Management programme is
(a) involving local communities in the management and restoration of degraded forests.
(b) involving rich people in conservation of forests.
(c) involving backward communities to conserve wildlife.
(d) involving the farmers to plant trees.
24. What is the name given to the forests of God and Goddesses?
(a) Sacred Garden
(b) Sacred Groves
(c) Sacred Park
(d) Sacred Orchards
25. Which one of the following statements is not true with regard to depletion of flora and fauna ?
(a) Land required for housing
(b) Agricultural expansion
(c) Mining activities
(d) Shifting agriculture
26. Which one of the following is not a reason for environmental destruction ?
(a) Global warming
(b) Unequal access
(c) Over population
(d) Inequitable consumption of resources
27. The biological loss is strongly correlated with the loss of cultural diversity because
(a) it has impoverished many indigenous and forest dependent communities.
(b) it has caused serious health problems for women.
(c) it has aggravated many natural hazards that affected the poor.
(d) All of the above
28. Which Wildlife Protection Act has included for the first time the list of protected species of plants ?
(a) Wildlife Protection Act of 1980
(b) Wildlife Protection Act of 1986
(c) Wildlife Protection Act of 1991
(d) Wildlife Protection Act of 1995
29. What is the position of India in the world in terms of bio-diversity ?
(a) First
(b) Fifth
(c) Tenth
(d) Twelve
30. The present forest cover of India in terms of the total geographical area is
(a) 18 per cent
(b) 19.39 per cent
(c) 22 per cent
(d) 15 per cent
31. In which of the following states has the Joint Forests Management started ?
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Orissa
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Arunachal Pradesh
32. Flora refers to
(a) Animal kingdom
(b) Plant kingdom
(c) Insects
(d) Flowers
33. Immensely rich in wildlife and cultivated species, diverse in form and function but closely integrated in a system is called
(a) Bioreserve
(b) Diversity
(c) Biodiversity
(d) Biome
34. The total number of plant species in India is
(a) 49000
(b) 47000
(c) 45000
(d) 81000
35. The total number of animal species in India is
(a) 81000
(b) 89000
(c) 98000
(d) 18000
36. Species which are in danger of extinction are called ……………..
(a) Endemic Species
(b) Extinct Species
(c) Vulnerable Species
(d) Endangered Species
37. Species which are no longer found on the earth are called
(a) Normal Species
(b) Vulnerable Species
(c) Rare Species
(d) Extinct Species
38. Which one of the river valley projects has significantly contributed to the loss of forests ?
(a) Nagarjuna Sagar
(b) Narmada Sagar
(c) Nizam Sagar
(d) Rana Pratap Sagar
39. Which state of India has the maximum area under reserved forests ?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Arunachal Pradesh
(d) Himachal Pradesh
40. The state having highest percentage of protected forests is
(a) Punjab
(b) Tamil Nadu
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
41. Project Tiger was launched in the year
(a) 1980
(b) 1973
(c) 1974
(d) 1975
42. In which of the following states is the Corbett National Park
(a) West Bengal
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Uttaranchal
(d) Madhya Pradesh
ANSWERS
JNV Chapter IV: VMC MCQs Chapter IV: Vidyalaya Management Committee (VMC) - MCQs Test your un...