Choose the correct option:
Question 1.
The number of seats reserved for women in the panchayats and municipalities is
(a) one-fourth
(b) one-third
(c) half
(d) one-fifth
Answer
Answer: (b) one-third
Question 2.
‘Holding together federations are not found in
(a) India
(b) Spain
(c) Belgium
(d) Australia
Answer
Answer: (d) Australia
Question 3.
Subjects like computer software comes in the
(a) Union List
(b) State List
(c) Concurrent List
(d) Residuary List
Answer
Answer: (d) Residuary List
Question 4.
Which of the following states has been given a special status?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir
(b) Tripura
(c) Bihar
(d) Haryana
Answer
Answer: (a) Jammu and Kashmir
Question 5.
The number of Scheduled Languages in India is
(a) 21
(b) 22
(c) 23
(d) 25
Answer
Answer: (b) 22
Question 6.
Which one of the following States in India has its own Constitution?
(a) Uttarakhand
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) J & K
(d) Nagaland
Answer
Answer: (c) J & K
Question 7.
Which among the following are examples of ‘Coming together federations’?
(a) India, Spain and Belgium
(b) India, USA and Spain
(c) USA, Switzerland and Australia
(d) Belgium and Sri Lanka
Answer
Answer: (c) USA, Switzerland and Australia
Question 8.
In India’s federal system, the state governments have the power to legislate on all those subjects which are included in the:
(a) Union list
(b) State list
(c) Concurrent list
(d) Residuary subjects
Answer
Answer: (b) State list
Question 9.
The Constitution of India
(a) divided powers between centre and states in three lists.
(b) divided powers between centre and states in two lists.
(c) listed the powers of the states and left the undefined powers to the state.
(d) Specified the pow ers of the states and left the residuary powers with the centre.
Answer
Answer: (a) divided powers between centre and states in three lists.
Question 10.
In case of a clash between the laws made by the centre and a state on a subject in the concurrent list:
(a) the state law prevails.
(b) the central law prevails.
(c) both the laws prevail within their respective jurisdictions.
(d) the Supreme Court has to intervene to decide.
Answer
Answer: (b) the central law prevails.
Question 11.
What is the third tier of government known as?
(a) Village Panchayats
(b) State government
(c) Local self-government
(d) Zila Parishad
Answer
Answer: (c) Local self-government
Explanation:
The third tier of government known as the local self-government. Local government is the best way to realise one important principle of democracy, namely local self-government.
Question 12.
What is true regarding sources of revenue in a federal system?
(a) States have no financial powers or independent sources of revenue.
(b) States are dependent on revenue or funds on the central government.
(c) Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
(d) States have no financial autonomy.
Answer
Answer: (c) Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
Explanation:
Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
Question 13.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding a unitary government?
(a) There is either only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government.
(b) The central government can pass on orders to the provincial government.
(c) A state government is conservable to central government.
(d) The powers of state governments are guaranteed by the Constitution.
Answer
Answer: (d) The powers of state governments are guaranteed by the Constitution.
Explanation:
Under the unitary system, either there is only one level of government or the sub-units are subordinate to the central government. The central government can pass on orders to the provincial or the local government and state government is conservable to central government.
Question 14.
What are the kinds of routes through which federations have been formed?
(a) One route involves independent states coming together on their own to form a bigger unit
(b) The second route is where a large country decides to divide its powers between the states and the national government
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Both a and b
Explanation:
There are two kinds of routes through which federations have been formed. The first route involves independent States coming together on their own to form a bigger unit, so that by pooling sovereignty and retaining identity they can increase their security.
Question 15.
Which period saw the rise of regional political parties in many states of the country?
(a) Period after 1990
(b) Period after 2000
(c) Period after 1980
(d) Period after 1970
Answer
Answer: (a) Period after 1990
Explanation:
All this changed significantly after 1990. This period saw the rise of regional political parties in many States of the country. This was also the beginning of the era of coalition government at the Centre.
Question 16.
Which language is recognised as the national language by the Constitution of India?
(a) Hindi
(b) English
(c) Tamil
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Explanation:
Our Constitution did not give the status of national language to any one language. Hindi was identified as the official language. But Hindi is the mother tongue of only about 40 percent of Indians.
Question 17.
Which state of India enjoys a special status and has its own Constitution?
(a) Bihar
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Kerala
(d) Jammu and Kashmir
Answer
Answer: (d) Jammu and Kashmir
Explanation:
Jammu and Kashmir has its own Constitution. Many provisions of the Indian Constitution are not applicable to this State. Indians who are not permanent residents of this State cannot buy land or house here.
Question 18.
Which of the following subjects is not included in the Union list?
(a) Defence
(b) Foreign affairs
(c) Police
(d) Banking
Answer
Answer: (c) Police
Explanation:
Union List includes subjects of national importance such as defence of the country, foreign affairs, banking, communications and currency.
Question 19.
Which of the following is not an example of ‘holding together’ federations?
(a) India
(b) Spain
(c) Belgium
(d) Switzerland
Answer
Answer: (d) Switzerland
Explanation:
A large country decides to divide its power between the constituent States and the national government. India, Spain and Belgium are examples of this kind of ‘holding together’ federations.
Question 20.
Which level of government in India has the power to legislate on the ‘residuary’ subjects?
(a) Union government
(b) State government
(c) Local self-government
(d) Both a and b
Answer
Answer: (a) Union government
Explanation:
According to our constitution, the Union Government has the power to legislate on these ‘residuary’ subjects.
Picture-based Questions:
Look at the following cartoons taken from NCERT Textbook page 21 and answer the question that follow:
The States Plead for More Powers

Perils of Running a Coalition Government
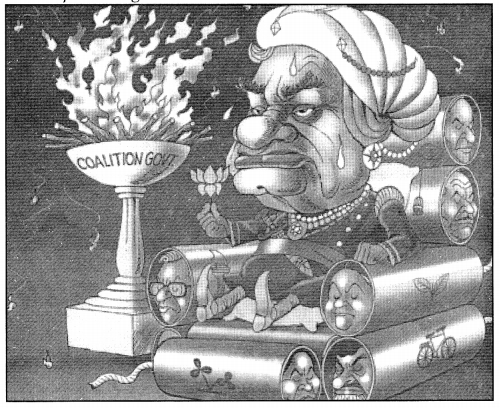
Question:
The above two cartoons show the relationship between Centre and States. Should the State go to the Centre with a begging bowl? How can the leader of a coalition keep the partners of government satisfied?
Answer
Answer:
The State should not go to the Centre in such a manner. Ours is a federal country and the principle of federalism works on the power sharing arrangement. The two levels of government i.e., the Centre and State governments have their own jurisdiction in specific matters of legislation, taxation and administration. Hence, the centre cannot order the State government to do something, nor can it stop them from ensuring their rights as autonomous federal units.
The leader of the coalition should accommodate different groups and factions in his/her party as well as among alliance partners. He/she should heed to the views and positions of the coalition partners and do accordingly.
Federalism Class 10 Quiz
Please fill the above data!
Name : Apu
Roll : 9
Total Questions:
Correct: | Wrong:
Attempt: | Percentage:
Q1. …………. is a system of government in which the power is divided between a central authority and various constituent units of the country?
A. Dictatorship
B. Unitary system
C. Monarchy
D. Federalism
Q2. How many levels of government does a federation usually have?
A. Single
B. Two
C. Three
D. Multiple
Q3. How many countries in the world have a federal political system?
A. 42
B. 33
C. 25
D. 18
Q4. In a federal system, the central government ………. order the state government to do something?
A. A & C
B. May
C. Cannot
D. Can
Q5. State government has powers of its own for which……..
A. It is answerable to Central government
B. It is not answerable to Central government
C. It is answerable to the people
D. B & C Q6. Different tiers of government govern the same citizens, but each tier has its own ………….. in specific matters.
A. Administration
B. Jurisdiction
C. Execution
D. Policies
Q7. Can the fundamental provisions of the constitution be unilaterally changed by one level of government in federalism?
A. Yes
B. No
C. May be in special provisions
D. A & C
Q8. When independent states come together on their own to form a bigger unit, so that by pooling sovereignty and retaining identity they can increase their security. This type of ‘coming together’ federations are practiced by which countries?
A. Switzerland & Canada
B. USA and Britain
C. USA, Australia and Switzerland
D. Britain, Canada, USA
Q9. Where a large country decides to divide its power between the constituent states and the national government. It is called ‘holding together’ federations. Which countries practice this system?
A. India, Pakistan, Italy
B. India, Spain, Belgium
C. Canada, Italy, Germany
D. Australia, Canada, USA
Q10. Which one comes under the Union List in India?
A. Police
B. Agriculture
C. Banking
D. Trade
Q11. Which one comes under the State List in India?
A. Defence
B. Currency
C. Communications
D. Police
Q12. On which given subject can both the Union as well as the State Governments make laws?
A. Currency
B. Defence
C. Trade Unions
D. Agriculture
Q13. What is meant by residuary subjects?
A. Subjects under union list
B. Subjects under state list
C. Subject under both state and union list
D. Subjects which are not under any list
Q14. Give an example of a subject under the residuary list?
A. Currency
B. Irrigation
C. Computer software
D. Commerce
Q15. States such as Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram enjoy special powers under certain provisions of the Constitution of India (Article 371), under which context do they get these provisions?
A. Because of trade and commerce
B. Protection of land rights of indigenous people
C. Special provisions for agriculture
D. For Defence purposes
Q16. Give one feature of Union territories?
A. They have powers of a state
B. They enjoy independent power
C. The Central Government has special powers in running these areas.
D. These are areas which are too small to become an independent State but which can be merged with any of the existing States
Q17. Sharing of power between the Union Government and the State governments is basic to the structure of the Constitution. The Parliament cannot on its own change this arrangement. Any change to it has to be first passed by both the Houses of Parliament with at least ………. majority?
A. 50 %
B. Three- fourth
C. Two- third
D. 25%
Q18. The creation of ………….. was the first and a major test for democratic politics in our country
A. States according to religion
B. States according to culture
C. Linguistic states
D. States according to topography
Q19. On which basis were states like Nagaland, Uttarakhand and Jharkhand created?
A. On the basis of language
B. On the basis of culture, ethnicity
C. On the basis of religion
D. On the basis of commerce and trade
Q20. Hindi is the mother tongue of only about …… percent of Indians?
A. 60%
B. 30%
C. 40%
D. 50%
Q21. Besides Hindi, there are __ other languages recognised as Scheduled Languages by the Constitution?
A. 21
B. 23
C. 27
D. 24
Q22. When was the beginning of the era of Coalition Governments at the Centre which led to a new culture of power sharing and respect for the autonomy of State Governments?
A. 1980s
B. 1990s
C. 1870s
D. 2000 onward
Q23. Census of India held in 2011, recorded more than ………distinct languages which people mentioned as their mother tongues?
A. 200
B. 500
C. 1200
D. 1300
Q24. In the data for Scheduled Languages of India which is the second highest in proportion of speakers (%) after Hindi?
A. Telugu
B. Tamil
C. Bengali
D. Urdu
Q25. As for English, only ……….per cent Indians recorded it as their mother tongue?
A. 20%
B. 5%
C. 0.5 %
D. 0.02%
Q26. The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
A. National government gives some powers to the provincial governments.
B. Power is distributed among the legislature, executive and judiciary.
C. Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
D. Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Q27. Consider the following two statements.
1. In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly demarcated.
2. India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
3. Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
4. India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies.
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1, 3 and 4
C. 1 and 2 only
D. 2 and 3 only
Q28. Federal power sharing in India needs another tier of government below that of the State governments, it is called………..
A. State offices
B. District government
C. Local government
D. Tehsils
Q29. When was the constitution amended to make the third-tier of democracy more powerful and effective?
A. 1990
B. 1992
C. 1989
D. 1993
Q30. In the local government elections at least ……… of all positions are reserved for women?
A. One – third
B. Two- third
C. 50%
D. 25%
Answer key for Class 10 Political Science Book Chapter 2 “Federalism” MCQs
Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans. Q. No. Ans.
1 D 11 D 21 A
2 B 12 C 22 B
3 C 13 D 23 D
4 B 14 C 24 C
5 D 15 B 25 D
6 B 16 C 26 B
7 B 17 C 27 C
8 C 18 C 28 C
9 B 19 B 29 B
10 C 20 C 30 A

No comments:
Post a Comment